Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Nephrology/AKI 1
39 - Introduction of Human Milk Fortifier and the Development of Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 39
Publication Number: 39.1791
Publication Number: 39.1791

Chelsea Young, MD (she/her/hers)
Pediatric Nephrology Fellow
Yale-New Haven Hospital
Cheshire, Connecticut, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm infants are at risk for early acute kidney injury (AKI) due to tubular immaturity leading to a decreased ability to handle increased solute load. Human milk fortifier (HMF) feeding with 2.5 g/100 kcal protein and 2.9 mEq/dL potassium is a standard supplement for this population. With a revised feeding protocol, HMF introduction occurred in the first week of life with a clinical perception that HMF introduction related temporally to AKI.
Objective: To determine the presence of AKI in the immediate period post HMF introduction in the VLBW preterm infants.
Design/Methods: AKI was defined using KDIGO 2012 guidelines. Week of life HMF introduction occurred was grouped into three categories (first, second, third week). The incidence of AKI was estimated and compared by timing of HMF introduction. Bootstrap 95% confidence interval was utilized.
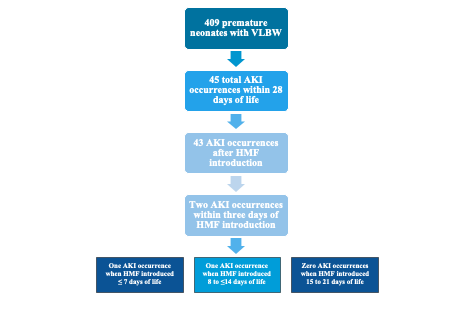
Results: Among 409 VLBW preterm infants in the NICU, 273 infants (66.8%) had HMF introduced within the first week, 113 infants (27.6%) within the second week, and 23 infants (5.6%) within the third week (Table 1). Within these 409 infants, 45 occurrences of AKI occurred within 28 days and 43 occurred after HMF introduction. Two kidney injuries occurred within three days of HMF introduction, one when HMF was introduced within the first week and one when HMF was introduced in the second week (Figure 1). Therefore, 2/409 premature infants in the NICU developed an AKI within three days of HMF introduction with an incidence rate of 0.49% (95% CI, 0.06%, 1.76%). When stratified by the timing of HMF exposure, 1/273 infants developed an AKI when HMF was introduced within the first week with an incidence rate of 0.37% (95% CI, 0.009%, 2.02%); 1/113 infants developed an AKI when HMF was introduced within the second week with an incidence rate of 0.89% (95% CI, 0.22%, 4.8%); 0/23 infants developed an AKI when HMF was introduced within the third week. Both infants who developed AKI within three days of HMF introduction were extremely preterm, extremely low birth weight males who developed sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis during the course of their NICU stay. They were also exposed to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and nephrotoxic antibiotics (Table 2).
Conclusion(s): In VLBW infants fortified with HMF, we found a low incidence of acute kidney injury both when HMF is introduced as well as in the immediate period after HMF introduction. Therefore, early introduction of HMF in preterm infants is unlikely to increase the risk of developing an acute kidney injury.
.png)
.png)
