Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Quality Improvement 5
74 - Antibiotic Stewardship and Cost Reduction through Quality Improvement in a Military Institution Nursery
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 74
Publication Number: 74.3083
Publication Number: 74.3083

Kevin M. Brinkman, MD (he/him/his)
Pediatric Resident
San Antonio Uniformed Services Health Education Consortium
San Antonio, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: A recent retrospective study at Brooke Army Medical Center (BAMC) showed a clinically significant reduction in sepsis evaluation when comparing routine clinical practice using the categorical risk assessment tool with the Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis Calculator in a cohort of infants with zero cases of culture-proven early onset sepsis (EOS). Antibiotic use when unnecessary has been shown to have adverse effects both short and long term. Use of the Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis Calculator has been shown to be both safe and effective in multiple studies with the potential to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use and lab evaluation.
Objective: The objective of this project is to reduce the rates of antibiotic use, CBC draws, and blood cultures on the BAMC nursery without worsening early onset sepsis rates or nursery readmission rates.
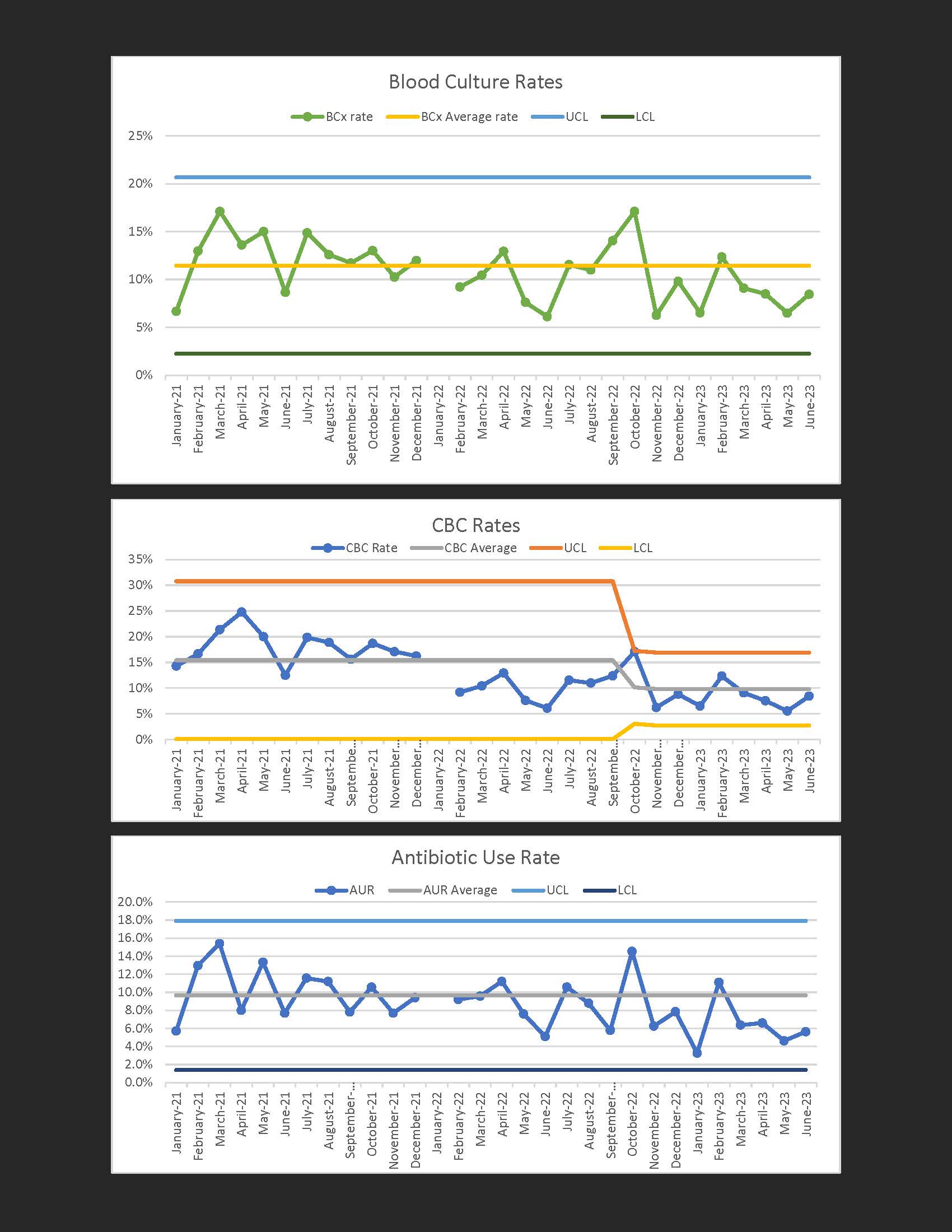
Design/Methods: Baseline antibiotic use rate (AUR), lab draws (CBC, blood culture), and EOS rate was reviewed retrospectively for the 1-year time period (July 2021- July 2022) prior to quality improvement (QI) intervention. The QI intervention involved implementation of the use of the Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis Calculator on the well newborn nursery and reduction of sepsis evaluation with antibiotics to 36 hours from 48 hours. Using Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles, this intervention was introduced in July 2022 with an objective to reduce lab evaluation by 10% and AUR by 5% by July 2023. Data during this time period was collected prospectively. Data was charted using SPC charts with clinically significant shifts or trends identified using Shewhart rules for process control with 6 points above or below the mean signifying a clinically significant trend and 8 points signifying a clinically significant shift. Once a shift or trend was identified, the mean was re-set using the data points that were responsible for the shift or trend. Upper and lower control limits were set 3 standard deviations from the mean.
Results: As of the 12-month intervention period of this PDSA cycle, a clinically significant reduction in CBC rates was observed with rates dropping from 15% to 10%. There was no statistically significant reduction in AUR or blood culture rate at this point. There was no change in overall rate of EOS or re-admission rate.
Conclusion(s): This QI intervention was able to reduce the rate of CBC draws without increased harm or other adverse effects, which allows for cost reduction in this military institution. Antibiotic use rate has not changed.