Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Cardiology and Pulmonary Hypertension 3: Pulmonary Hypertension and Prematurity
105 - Circulating miRNA Signatures Associated with Echocardiographic Evidence of Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Infants Born Less Than 32 Weeks Gestation
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 105
Publication Number: 105.1983
Publication Number: 105.1983

Marjorie M. Makoni, MD., MS
Associate Professor
OUHSC/OU Health
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Pulmonary vascular disease (PVD) is a common complication of prematurity and is associated with chronic lung disease. Early detection of PVD can be accomplished by targeted neonatal echocardiography (TnECHO). Recent studies have identified altered microRNAs (miRs) thought to contribute to the development and progression of chronic lung disease in preterm infants. The detection of a similar signature in premature infants at high risk for PVD would allow for the development of novel and targeted miR-based therapies.
Objective: Our objective was to determine serum-based miR signatures associated with echocardiographic evidence of PVD in preterm infants between postnatal day (DOL) 28 and 36 wks postmenstrual age (PMA).
Design/Methods: We conducted a prospective cohort study of infants born ≤ 32 wks gestational age. Infants underwent TnECHO and blood draws at DOL 28 and 36 wks PMA. Subjects were categorized according to echo-derived estimate of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), a ratio of right ventricular ejection time to pulmonary artery acceleration time: (1) High PVR (≥ 3.8) and (2) Normal PVR ( < 3.8). Three phenotypic subgroups were identified based on relative PVR at the DOL 28 and 36 wks PMA: Group 1: High PVR at DOL 28 and 36 wks PMA; Group 2: High PVR only at 36 wks PMA; and Group 3: Normal PVR at DOL 28 and 36 wks PMA. Expression data for 827 miRs were determined via the NanoString nCounter Human miRNA CodeSet Kit. Data preprocessing and differential expression analysis was conducted by NanoString nSolver 4.0 (p < 0.05 with log fold change(|logFC|>0.15)) for significantly different miR expression between DOL28 and 36 wks PMA. Putative miR targets were predicted using Qiagen Ingenuity Pathway Analysis.
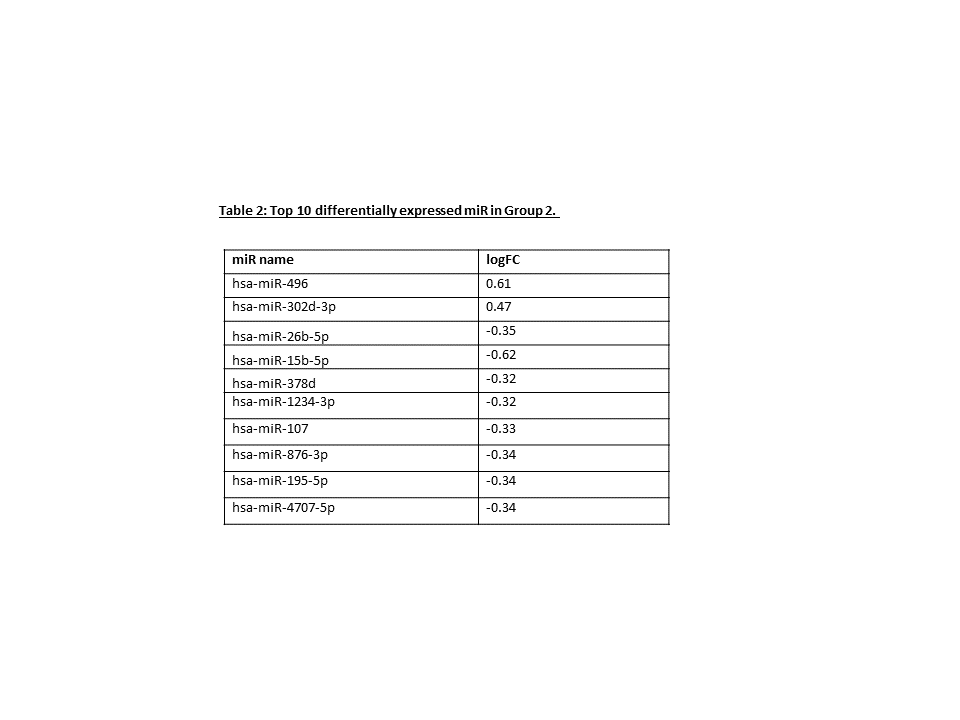
Results: A total of 36 preterm infants were enrolled [Group 1 (n=10); Group 2 (n=11); Group 3 (n=15 High PVR across both timepoints (Group 1) was associated with 36 unique miRs, including miR-371b-5p (0.28 logFC) and miR-451a (-1.6 logFC). Group 2 (normal PVR to high PVR) was defined by 39 miRs, including miR-15b-5p (-0.62 logFC) and miR-496 (0.61 logFC). Group 3 (normal PVR, both timepoints) was described by 9 unique miRs, including miR-627-5p (-0.45 logFC) and miR128-1-5p (0.45 logFC).
Conclusion(s): The unique and shared miR signatures referenced above include species previously described in association with pulmonary or vascular pathology. They may represent promising candidate biomarkers for development of PVD and serve as new therapeutic targets for therapies. RT-qPCR validation is pending, and future studies will aim to delineate their pulmonary/vascular messenger RNA and protein targets.