Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 1
595 - Regulatory Profile of Human Preterm Umbilical Cord Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Exposed to Maternal Marijuana and Active SARS-CoV-2 Infection at Delivery
Friday, May 3, 2024
5:15 PM - 7:15 PM ET
Poster Number: 595
Publication Number: 595.398
Publication Number: 595.398
- AI
Adnan Ismail, MD (he/him/his)
Neonatologist
CHOC Children's Hospital of Orange County
Irvine, California, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: COVID-19 caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus has led to a worldwide pandemic with oxidative stress, inflammatory cascade, and cytokine storm as main causes of morbidity and mortality. It is known that pregnant women are at higher risk of viral infections given an alteration in immune response. Mothers who smoke marijuana during pregnancy are even at higher risk. The infection varies from asymptomatic to severe disease in pregnant women depending upon the degree of inflammation and cytokine storm.
Objective: To determine the effects of simultaneous maternal marijuana smoking and SARS-CoV-2 infection on the biologic efficacy of human preterm umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
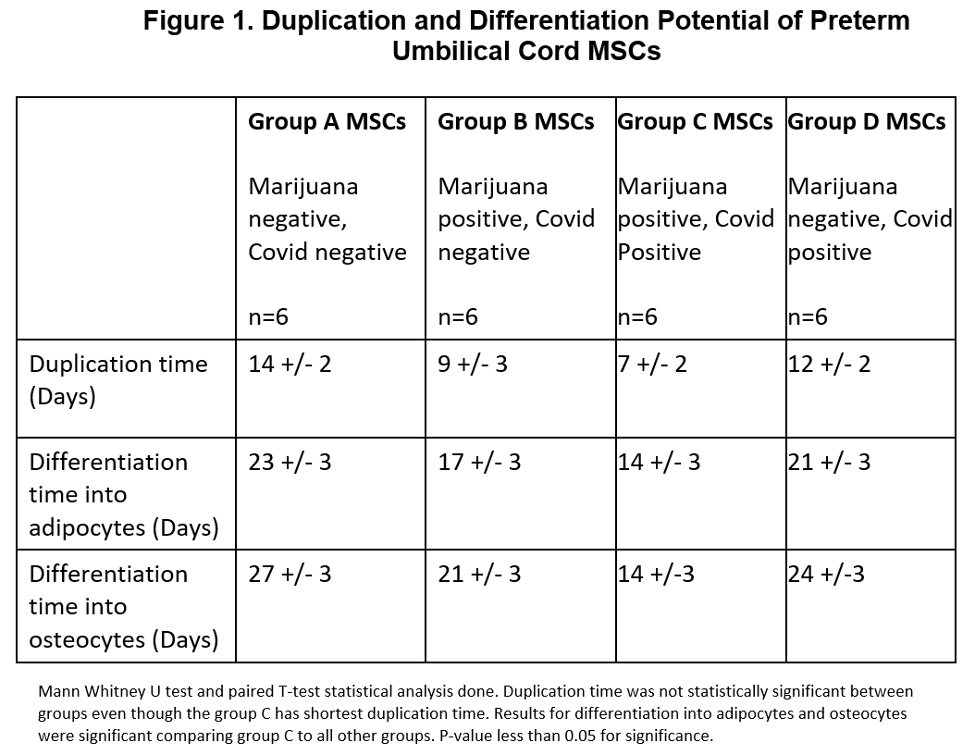
Design/Methods: The study was approved by the Institutional IRB. The umbilical cords at preterm delivery (24-28 weeks’ gestational age) were collected from four groups (n=6/group):
Group A: Normal (no marijuana use with negative SARS-CoV-2 infection)
Group B: Non-Covid Marijuana (Marijuana use with negative SARS-CoV-2 infection)
Group C: Covid Marijuana (marijuana use with positive SARS-CoV-2 infection)
Group D: Covid Non-Marijuana (no marijuana use with positive SARS-CoV-2 infection)
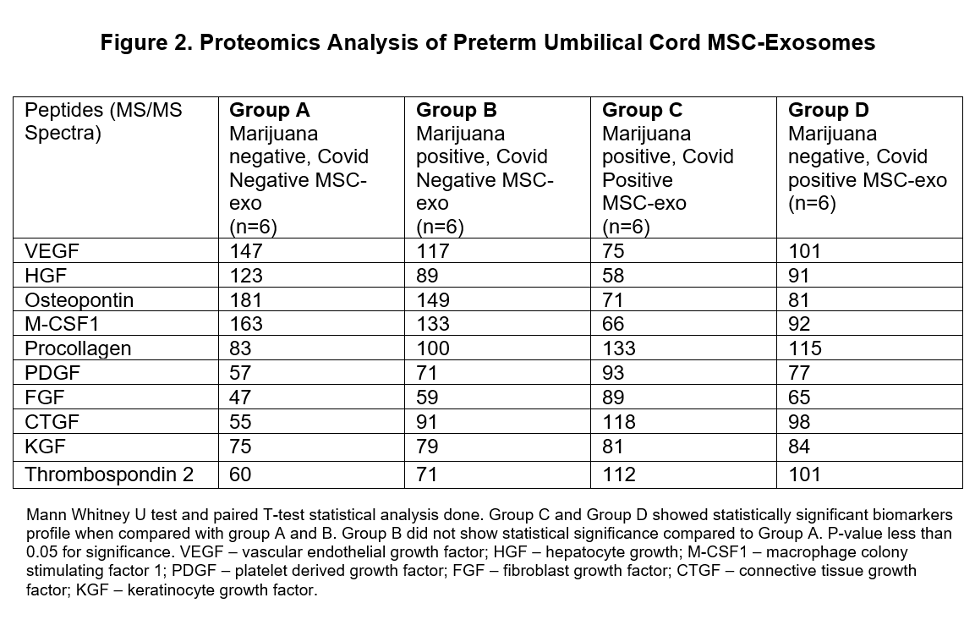
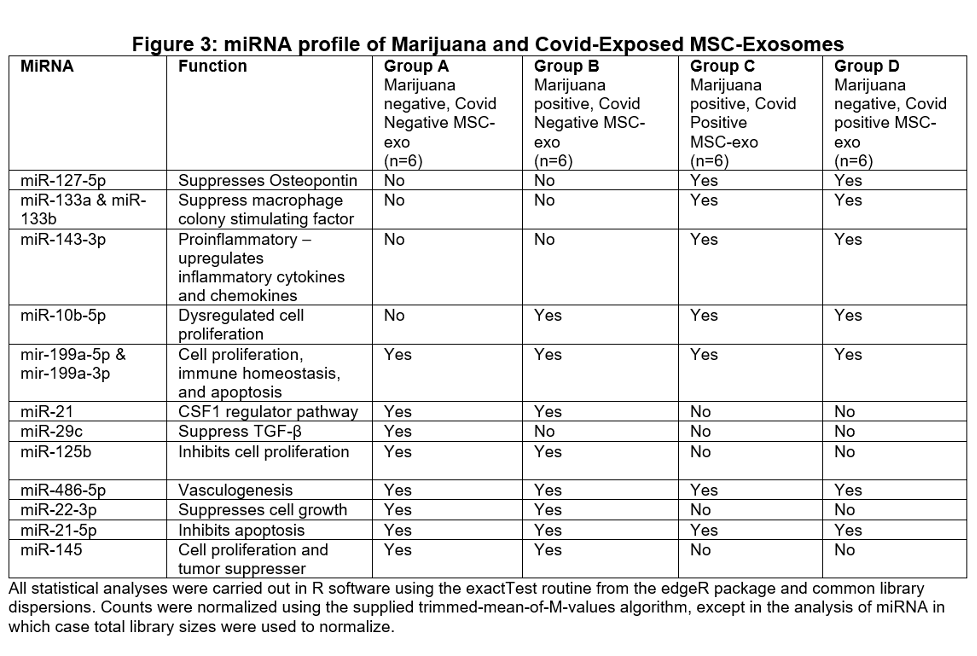
Marijuana use determined by positive maternal urine THC screen at delivery. Covid positive status determined by positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR at delivery. The umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly plastic adherent cells were harvested, propagated, and immunodepleted to obtain MSCs. MSC duplication and differentiation time assessed between four groups. MSC-Exosomes (MSC-exo) isolated per our laboratory published protocols. MSC-exo generated per our published protocols and proteomics analysis done to determine secreted biomarkers. MSC-exo microRNA (miRNA) levels determined using TaqMan RNA kits per manufacturer protocols.
Results: Group C (SARS-CoV-2 positive with positive Marijuana use) showed a much shorter duplication time and differentiation time (adipocytes and osteocytes) when compared with other groups (Figure 1). Proteomics analysis identified significantly lower lung vascular and epithelial injury preventive biomarkers concentration in Group C MSC-exo fraction compared to other groups MSC-exo fraction (Figure 2). Similarly, Group C MSC-exo fraction was deficient in lung injury and repair miRNAs when compared with other groups MSC-exo fraction (Figure 3). All results were statistically significant.
Conclusion(s): Maternal marijuana use and active SARS-CoV-2 infection at the time of delivery alters the biologic potential of human preterm umbilical cord derived MSC-exo with lack of protected biomarkers and regulatory miRNA leading to lung injury.