Infectious Diseases
Session: Infectious Diseases 1
582 - Outcomes Following Community Acquired SARS CoV 2 Infections for Patients with BPD
Friday, May 3, 2024
5:15 PM - 7:15 PM ET
Poster Number: 582
Publication Number: 582.478
Publication Number: 582.478

Melinda Ingram, APRN
BPD APN
Nationwide Children's Hospital
Columbus, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
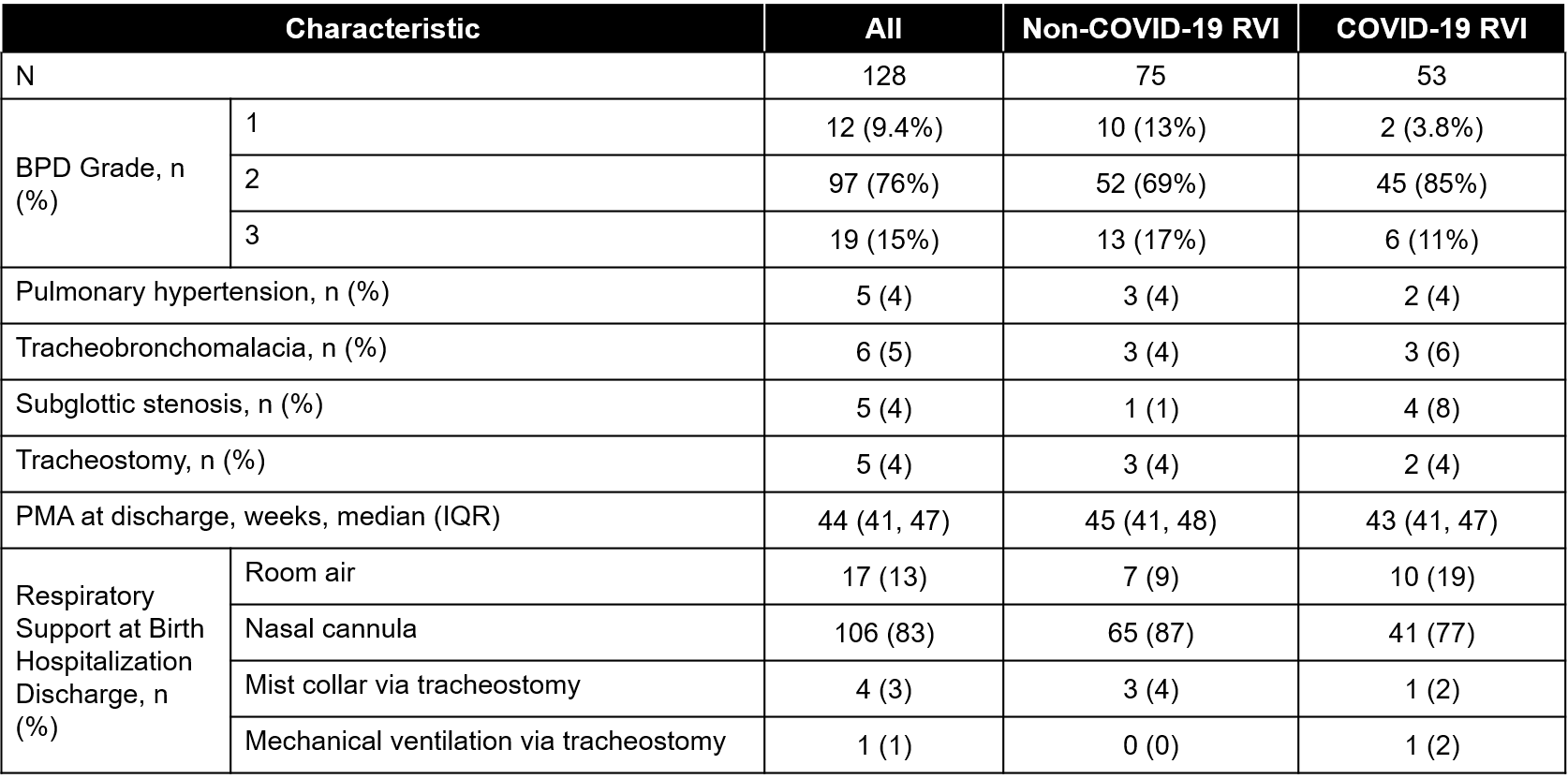
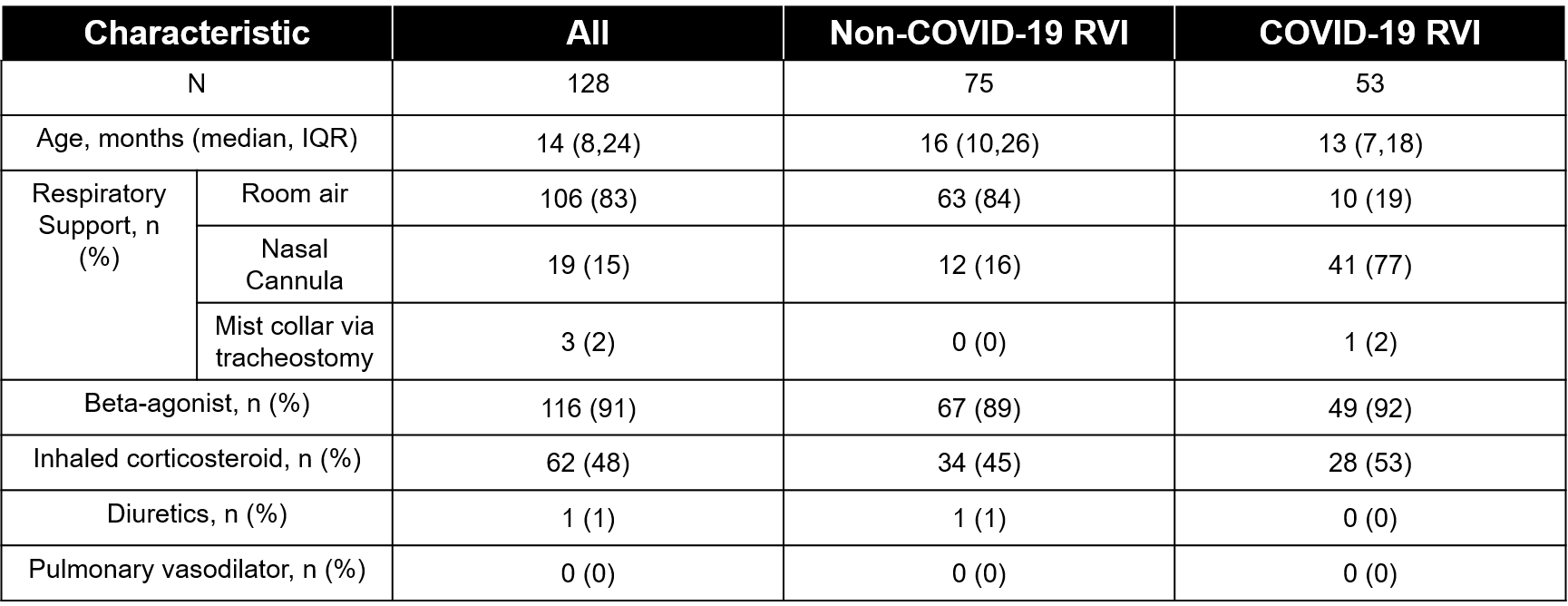
Background: The outcomes of patients with established bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) with community acquired COVID-19 compared to respiratory viral infections (RVI) of any other type remain unknown.
Objective: To compare death and hospitalization rates between infants and children with BPD and community-acquired COVID-19 and RVIs of any other type.
Design/Methods: Retrospective case series of patients with established BPD, defined by 2019 Neonatal Research Network criteria, followed by a multidisciplinary outpatient BPD program. Included patients with >= 1 unique visit to a BPD follow-up clinic between March 14, 2020 and June 30, 2022 diagnosed with a viral infection via laboratory testing. Clinical characteristics of patients were abstracted from the electronic medical record and presented using standard descriptive statistics.
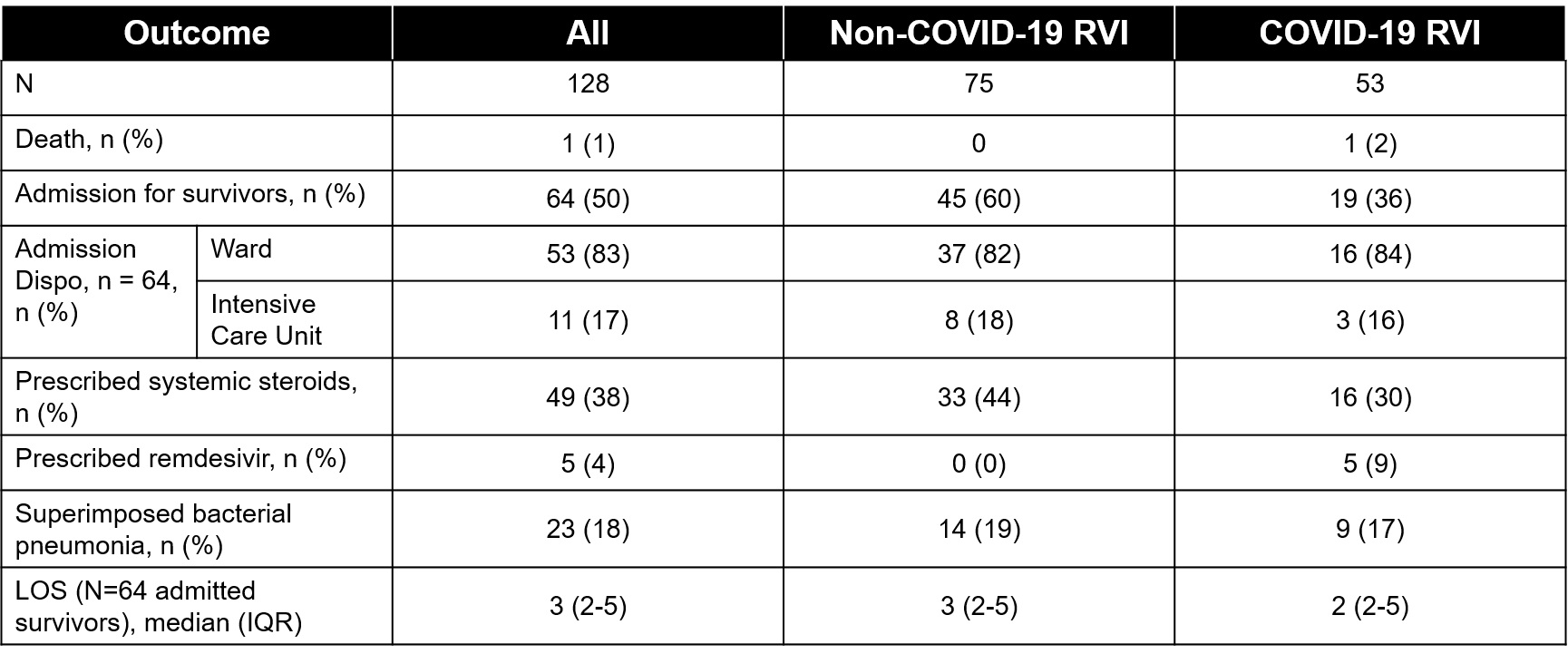
Results: 128 patients met BPD criteria and had one positive RVI during study period. 75 patients had non COVID-RVI and 53 patients had COVID-19. There was one death with COVID-19 RVI however infant had a decannulation at home. Of survivors, 60% non-COVID RVI patients were admitted to hospital vs 36% of COVID-19 RVI patients.
Conclusion(s): Patients with BPD are susceptible to community acquired COVID-19 infections following initial neonatal intensive care unit hospitalization. COVID-19 RVI is associated with less severe illness than non-COVID-19 RVI. Though most patients in this series had relatively benign clinical courses following infection, future studies are needed to determine effective prevention measures, including vaccine safety and efficacy, for patients with established BPD.