Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Nephrology/AKI 1
35 - Association between Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin and Proteinuria in Non-Cardiac Postoperative Neonates
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 35
Publication Number: 35.2158
Publication Number: 35.2158

Cara Slagle, MD (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor
Riley Children's Hospital and Indiana University Health
Westfield, Indiana, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Elevated urine microalbumin to urine creatinine (UMC) ratios have been associated with the progression of acute kidney injury (AKI) to chronic kidney disease. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) has demonstrated a better association with proteinuria compared to AKI in neonates.
Objective: We aimed to identify if the direct relationship between uNGAL and proteinuria persisted in infants following non-cardiac surgical procedures.
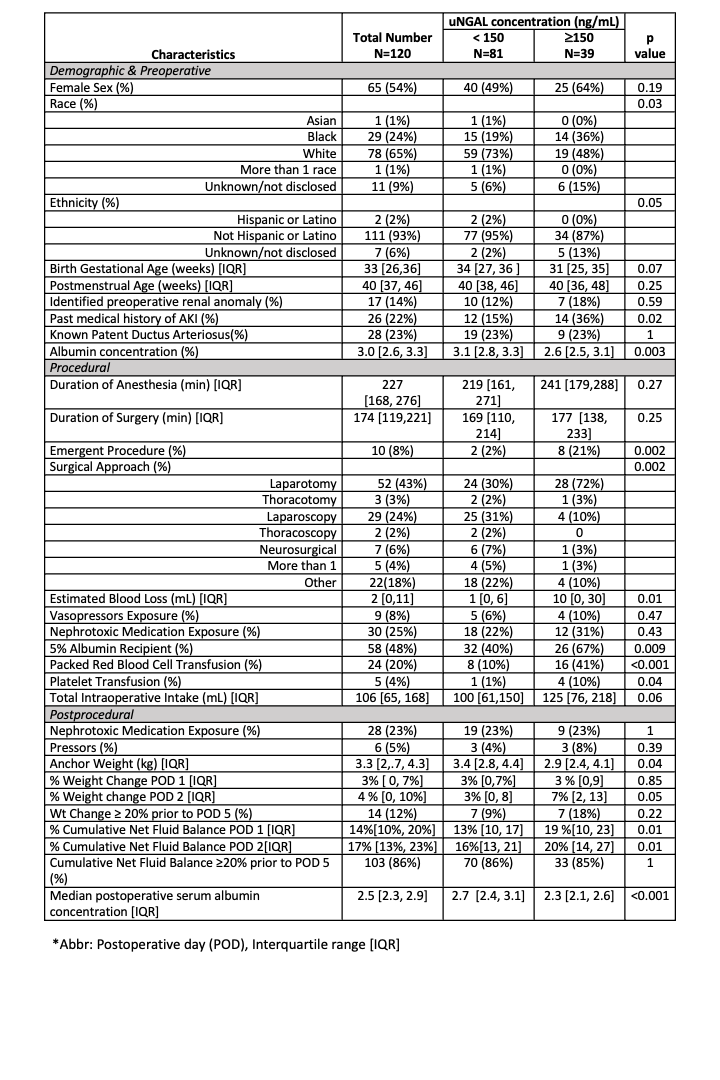
Design/Methods: Infants admitted to the Level IV NICU, < 1 year of age, and identified as needing non-cardiac surgical intervention were eligible for inclusion and prospectively enrolled. Urine was collected pre- and post-procedure at 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, and 96 hours. Data on demographics, procedure, and anesthesia characteristics, as well as post-procedural laboratory measures, were recorded to postoperative day 5. An a priori cutoff for elevated uNGAL was set at 150 ng/mL based on historical cohorts and progression to AKI. Descriptive statistics between the cohorts were used. Generalized additive mixed modeling (GAMM) was applied to evaluate changes in uNGAL and proteinuria over time.
Results: Ninety-one neonates underwent 120 non-cardiac surgical procedures providing 628 urine samples for analysis. There were 39 procedures with a postoperative elevated uNGAL (>=150 ng/mL) by 48 hours. Descriptive statistics of the cohort are presented in table 1. Proteinuria (>=0.2 mg/mg) was present in 83% of samples. Elevated uNGAL procedures were associated with increased urine concentrations of protein to urine creatinine (UPC) and UMC (UPC: 2.2 mg/mg [IQR: 1.4, 3.4] vs. 1.3 mg/mg [IQR: 0.9, 2.0], p= 0.0009; UMC: 251 mg/g [132, 757] vs. 168 mg/g [109, 295], p=0.0012). Figure 1 depicts UMC and UPC concentrations over perioperative time.
Conclusion(s): Proteinuria and microalbuminuria are common in neonates undergoing non-cardiac procedures. Postoperative elevated urine NGAL >=150 ng/mL before 48 hours is associated with higher urine protein to urine creatinine concentrations and urine microalbumin to creatinine concentrations.
.png)