Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Quality Improvement 6
98 - The Impact of a 5-day Bundle of Care on Severe Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH) in Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) newborns
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 98
Publication Number: 98.2804
Publication Number: 98.2804
- DA
Dimitrios Angelis, MD (he/him/his)
Neonatologist
University of Texas Southwestern Med
Dallas, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Severe IVH (grades 3 or 4 as per Papile classification) occurs in up to 20-40% of ELBW newborns. Use of a Bundle of Care (BoC), assures consistency of early nursing care, starting after birth at the delivery room or upon admission to the NICU. BoCs provide hemodynamic stability and could decrease the risk of IVH. Their duration ranges from 3 days to 7 days, with variability in its components. This study retrospectively analyzed all ELBW between 2016-2023 at a Level 3 NICU for severe IVH and mortality based on the type and duration of BoC.
Objective: To assess if quality improvement (QI) interventions involving modifications in BoC improve the rates of the following outcomes: All IVH, severe IVH -3 and 4, death as well as the composite/combined outcomes of severe IVH with death)- in ELBW. IVH was diagnosed with head ultrasounds (HUS) on 3-5, 7-10 day of life. Data were collected prospectively for the QI's needs and more detailed retrospectively after IRB approval.
Design/Methods: Pre-Intervention [Baseline, ERA 1] data were collected during a 2-year period (01/2016-12/2017). During this period various and not consistent nursing practices were used for early management of ELBW. Intervention: BoC ERA 2 included a 3-day BoC after birth: 1. neutral head (midline) and supine position, 2. head of bed elevation (15-30 degrees), 3. noise/Light reduction, 4. slow boluses etc. (01/2018-12/2020]. ERA 3: extension of BoC for 5 days, with additional use of Transcutaneous CO2 detectors (TCOMs) (01/2021-03/2023).
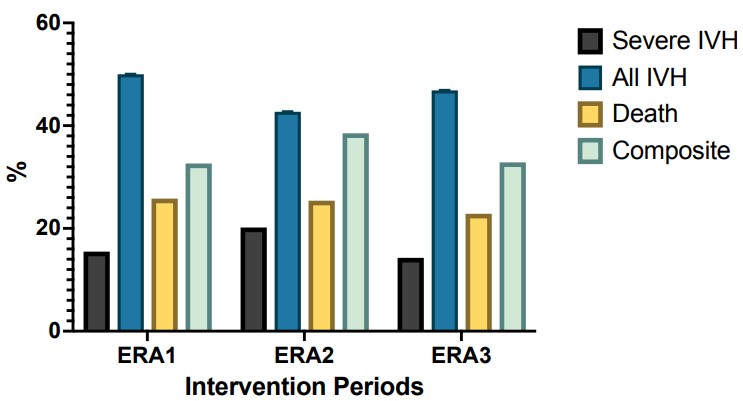
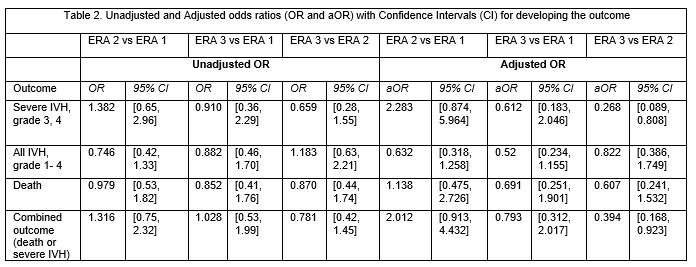
Results: Baseline characteristics among ERA1 vs 2 and 3 (Table1). Birth Weight (BW), Gestational Age (GA), antenatal steroids (AS) and APGAR at 5 min decreased in most recent ERA (3). In Figure 1 we present the unadjusted rates of each outcome (no significant differences noted). In Table 2 we present the unadjusted and adjusted odds ratios (aOR) for each outcome among ERAs. Logistic regression was performed to adjust for the following variables: GA, BW, gender, steroids and 5 -min APGAR. There was a significant reduction in aOR for developing severe IVH and the composite outcome after the implementation of the 5-day BoC [ERA3 vs 2, aOR, 95%CI 0.268 (0.089, 0.808) and 0.394 (0.168, 0.923) respectively].
Conclusion(s): Using a 5 -day BoC and TCOMs versus a 3– day BoC that places emphasis on neonatal position after birth may facilitate the stabilization (or potentially the reduction of severe IVH and/or death) in ELBW newborns, especially in an era of resuscitating newborns with decreasing GA. To our knowledge this is one of the few studies to assess efficacy of a 5-day BoC in a very high risk population of ELBW.
.jpg)
