Quality Improvement/Patient Safety
Session: Quality Improvement/Patient Safety 5
40 - A Quality Improvement Project to Improve Attendance Rates of Infants with Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) at birth to the NICU Follow Up Clinic
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 40
Publication Number: 40.2838
Publication Number: 40.2838

Subhash Puthuraya, MD
Dr
Cleveland Clinic Children's Hospital
Lerner College of Medicine and Cleveland Clinic Children's Hospital
Cleveland, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
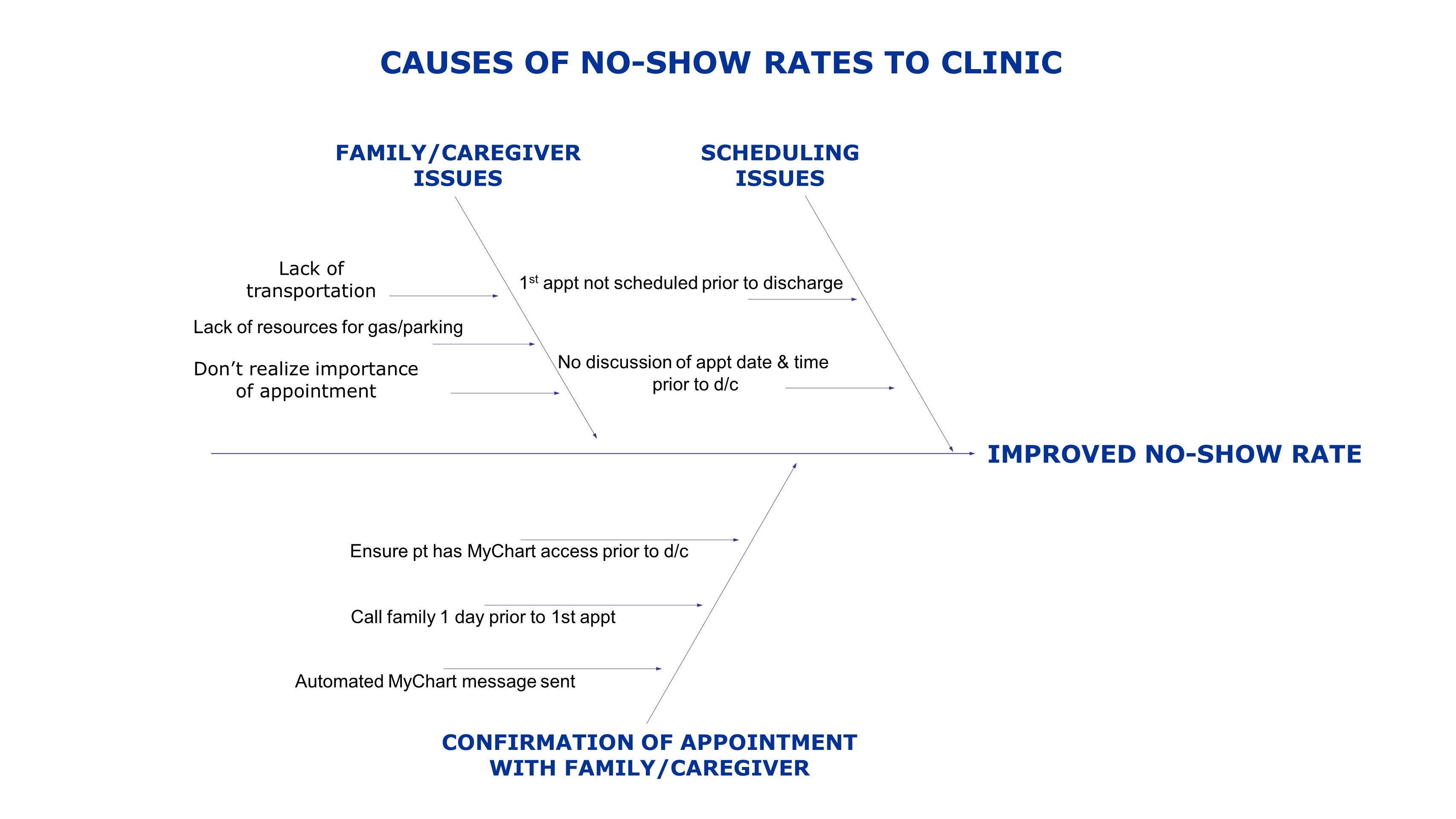
Background: Infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) at birth are at increased risk for brain injury and adverse neuro-developmental outcomes. Timely assessment of potential impairment can facilitate appropriate referral to physical, occupational and speech therapies, and to early
intervention programs. Attendance to the post-discharge NICU neurodevelopmental follow-up clinic can be as low as 55% resulting in many infants without the necessary assessment and referral for therapies.
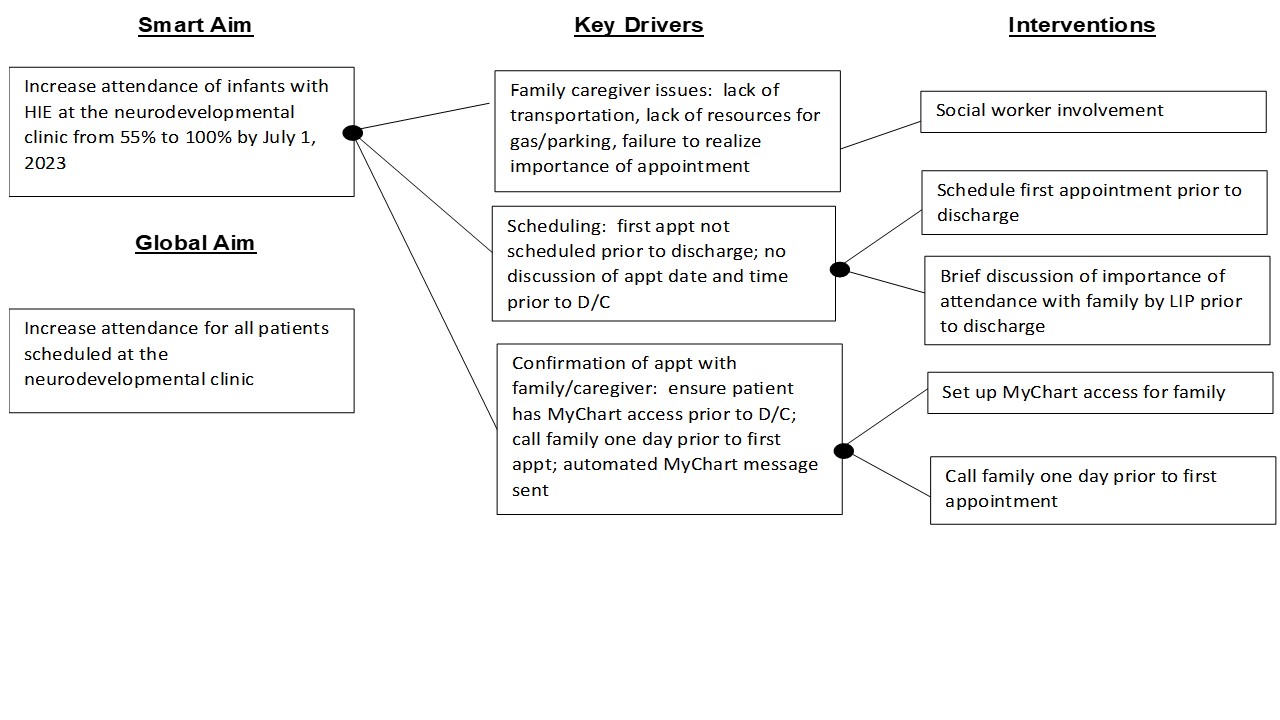
Objective: To describe outcomes from the QI project to improve the attendance to the clinic after initiating the intervention bundle and completing two Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles. Our SMART aim was to increase the attendance rate to the NICU follow-up clinic from 55% to >90% by 07/01/23 using a three-step intervention bundle
Design/Methods: All infants with HIE who received therapeutic hypothermia were followed at the NICU follow-up clinic. Baseline data was collected from infants with HIE born from 01/01/20 to 12/31/20 and those from 07/1/22 to 07/01/23 were included for the follow up rate. Institutional review board approved the project. In July 2022, an intervention bundle was implemented to improve the attendance rates.
The intervention bundle suggested by multidisciplinary team to assess the barriers included
1. Scheduling an appointment within 4 weeks following discharge and giving the date and time to the family/caregiver prior to discharge
2. Discussing with family/caregiver the importance of attending the appointment prior to discharge
3. Phone call to the family/caregiver one day prior to the appointment as a reminder as well as an EMR automated reminder.
Our outcome measure was the rate of attendance following the use of the intervention bundle.
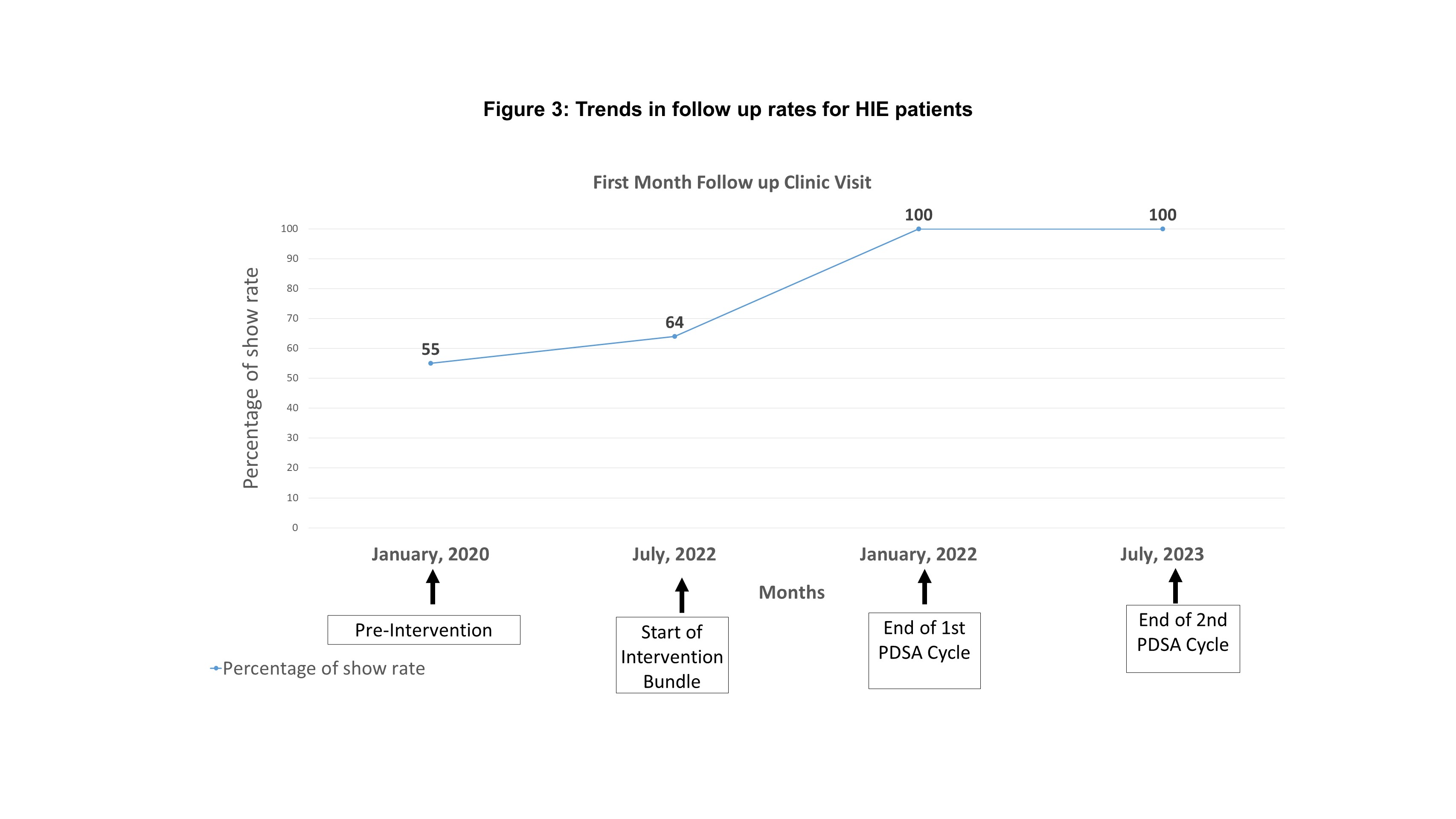
Results: • Twenty-four infants with HIE were included to calculate the baseline follow up rate. The baseline follow up rate was 64% for the first visit.
• In this ongoing project, ten patients were followed in the last one year and the first visit follow up rate has increased to 100%
• Additional barriers such as transportation issues, ready availability of outpatient appointment slots for rescheduling and availability of
telemedicine visits were identified in two PDSA cycles. The second PDSA cycle implemented in January 2023 incorporated solutions to these barriers to improve attendance rates
Conclusion(s): The HIE specific intervention bundle will improve the follow up rate in the Neurodevelopmental clinic.
Higher follow up rates will increase coordination with rehabilitation therapy services and thus improve the quality of care provided to these infants.