Neonatology
Session: Neonatal General 6: POCUS, Technology in NICU
148 - Describing X-ray Utilization Patterns in Neonates for POCUS-Appropriate Indications
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 148
Publication Number: 148.2160
Publication Number: 148.2160

Ravi Bhavsar, MD (he/him/his)
Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Fellow
University of Kentucky College of Medicine
Lexington, Kentucky, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Data regarding NICU radiation exposure is scarce, with no estimate for the number of radiographs performed on neonates of all gestational ages. Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) enhances procedural safety and offers high sensitivity and specificity for various diagnostic indications. POCUS has demonstrated the potential to reduce neonatal X-ray (XR) exposure. This study aims to outline X-ray utilization patterns in NICU-admitted neonates for indications that can be safely and accurately addressed with POCUS.
Objective: To describe patterns of XR use in the NICU for four specific clinical indications where POCUS is considered equivalent or superior for diagnosis.
Design/Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted on all inborn infants admitted to a large Level IV NICU and discharged between January 1 and December 31, 2022 who received at least 1 XR for either of four indications - central line insertion, endotracheal intubation, evaluation of respiratory distress and bowel gas pattern. Indication for each XR ordered was identified through EMR charting. Data was collected on the total number of x-rays administered during hospital stay, and clinical and demographic variables. Findings were reported using descriptive statistics and differences analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and student t-tests with p< 0.05 reported as significant.
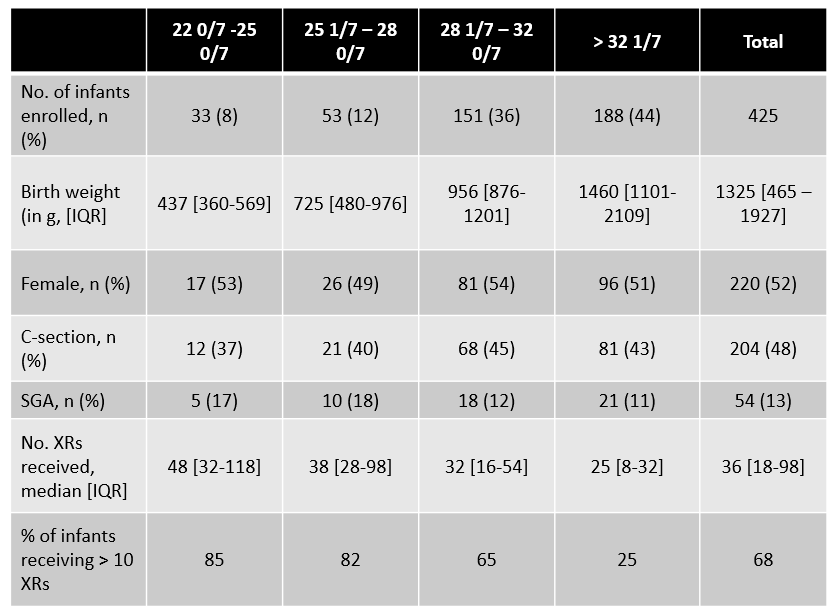
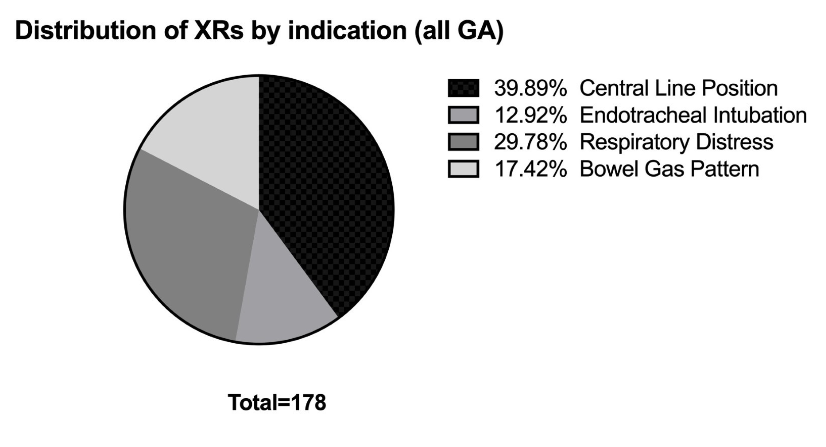
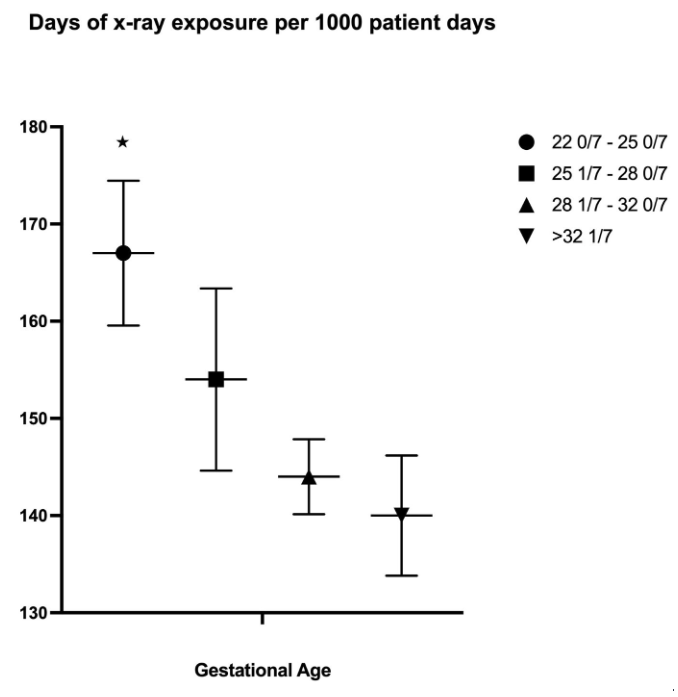
Results: A total of 425 infants were included with median birthweight 1325g [465 – 1927]. 58% of infants were < 32 weeks’ gestational age (wga) (Table 1). Median number of XRs received for select indications was 36 [18-98] with infants < 28 wga constituting 71% of all XRs. 68% of infants received more than 10 XRs. Verification of central line tip position accounted for 40% of all XRs (Figure 1). 60% of these were performed at the time of PICC line placement. Average days of XR exposure per 1000 patient days was 143.2, which was significantly higher in the 22 0/7 - 25 0/7 wga group (Figure 2).
Conclusion(s): We have described patterns of XR use in the NICU for four diagnostic and procedural indications where POCUS offers high sensitivity and specificity and could be used as a potential alternative. This research underscores the pressing requirement for widespread POCUS adoption to minimize X-ray exposure in premature infants.