Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical Science 3: Non-Invasive Respiratory Support, RDS
215 - The failure of RAM cannula for nasal continuous positive airway pressure (nCPAP) in extreme preterm infants with RDS and evolving BPD
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 215
Publication Number: 215.3198
Publication Number: 215.3198
- WK
Waleed Kurtom, MD
Neonatologist
UPMC Childrens Hospital of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The clinical significance and impact of RAM cannula nCPAP (RAM) use in extreme preterm infants that require prolonged respiratory support has not been fully evaluated.
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of RAM for respiratory support in a cohort of extreme premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and evolving bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
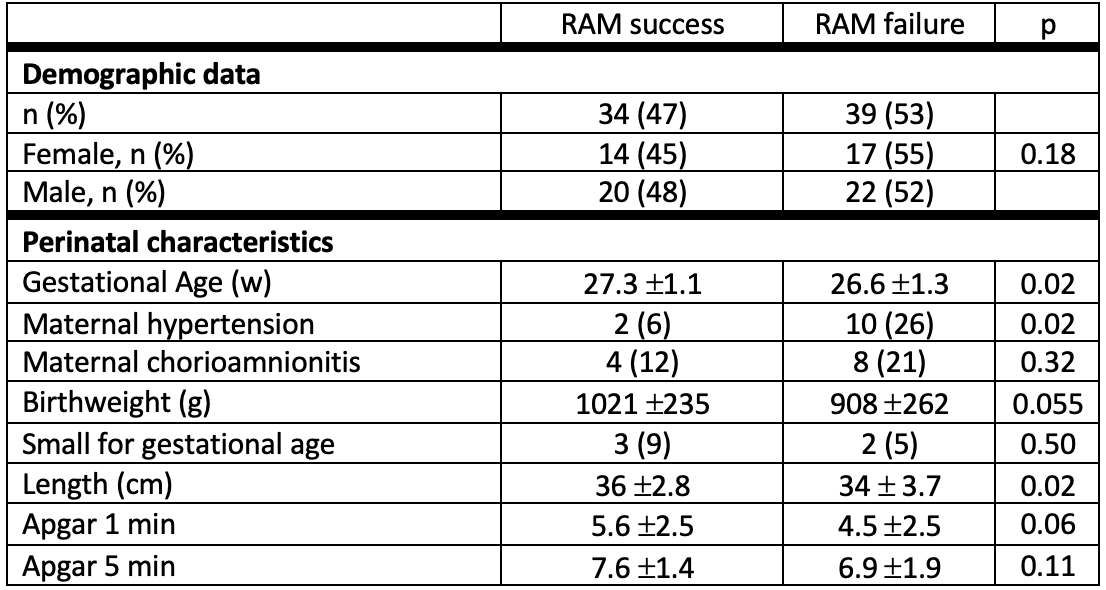
Design/Methods: This was a retrospective cohort of 73 infants, born < 28 weeks of gestation, who were supported with RAM after the first week and during their hospital course in the NICU at Hamot Hospital of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center between 2012-2022. RAM was used primarily as a weaning modality from higher levels of support. Data collection included prenatal and postnatal variables which were analyzed and segregated into RAM failure and success groups. RAM failure was defined as the need to escalate/re-establish respiratory support with bubble CPAP or invasive mechanical ventilation as determined by the clinical team. BPD was defined as FiO2 need at 36w PMA.
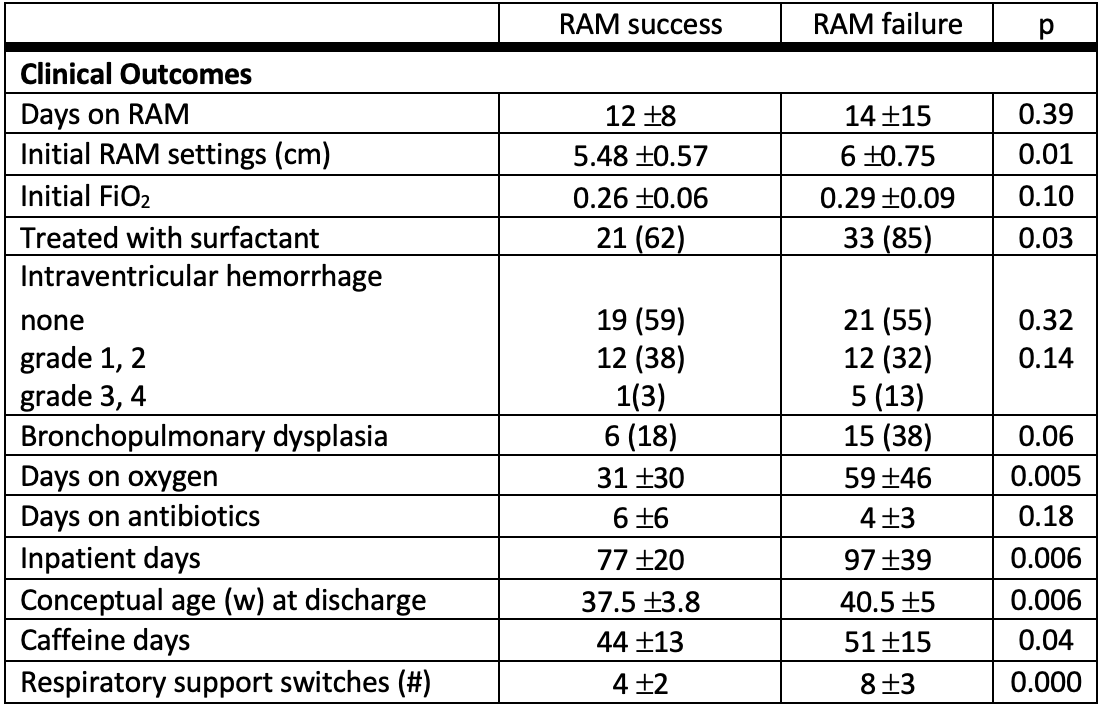
Results: Of the 73 infants in the cohort, 39 (53%) had RAM failure. Lower mean gestational age (GA) and maternal hypertension were factors associated with RAM failure (p= 0.02) (Table 1). Infants in the RAM failure group were initially treated more often with surfactant (p=0.03) (Table 2). The possible consequences of RAM failure included a longer duration of oxygen therapy and hospitalization (p < 0.01) (Table 2). The RAM failure group notably had more than twice as many respiratory support switches during their hospitalization than the success group (p < 0.001) (Table 2).
Conclusion(s): In this cohort of extreme premature infants, there were prenatal and postnatal factors associated with the probability of RAM failure. Our results show that RAM cannula support may only be successful in more mature infants with less severe lung disease, but its clinical significance and practical considerations need to be further investigated.