Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical Science 1: BPD, BPD Biomarkers and Diagnosis
185 - Early prediction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia at seven days of life in infants born before 30 weeks by clinical, ultrasonographic and proteomic data
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 185
Publication Number: 185.3095
Publication Number: 185.3095

Almudena Alonso-Ojembarrena, PhD (she/her/hers)
Neonatologist
Puerta del Mar University Hospital
San Fernando, Andalucia, Spain
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most important chronic respiratory disease related to prematurity, with important associated co-morbidities and increase risk of death. We lack an early diagnostic tool for this disease, so it is difficult to assay specific treatments to prevent it.
Objective: The aim of this study is to analyze the diagnostic accuracy of a multiparametric approach to predict BPD as soon as the first week of life in infants born before 30 weeks of gestational age (GA).
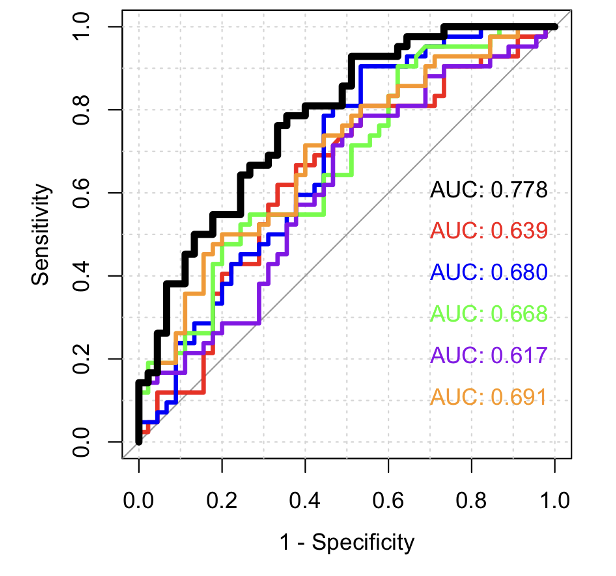
Design/Methods: This is a multicentric study, in which we performed a lung ultrasound (LU) and a nasopharyngeal aspirate (NPA) at seven days of life in infants born before 30 weeks’ GA. We also gathered data on clinical and respiratory variables measured before this age. We calculated lung ultrasound score and analyzed the number of consolidations and type of pleural line in LU scan; high-throughput mass spectrometry-based proteomics was applied to NPA with posterior bioinformatic approach for protein differential expression, functional enrichment, and predictive analyses. We calculated the area under the curve (AUC) for each predictor alone or combined between them
Results: We included 138 patients from seven NICUs, with a median gestational age of 27 weeks (interquartile rank (IQR) 26-28 weeks), and birthweight 990g IQR 837-1150g). From the whole cohort, 16 infants (12%) died before reaching 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age, 20 developed grade 1 BPD (14%), 22 had grade 2 BPD (16%), and 3 (2%) had grade 3 BPD.
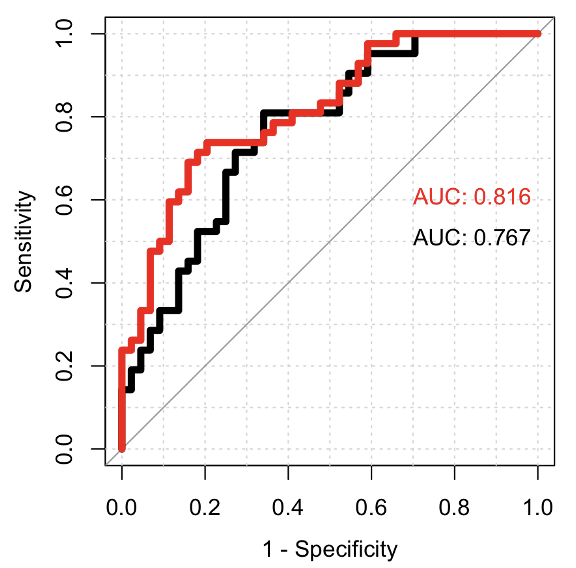
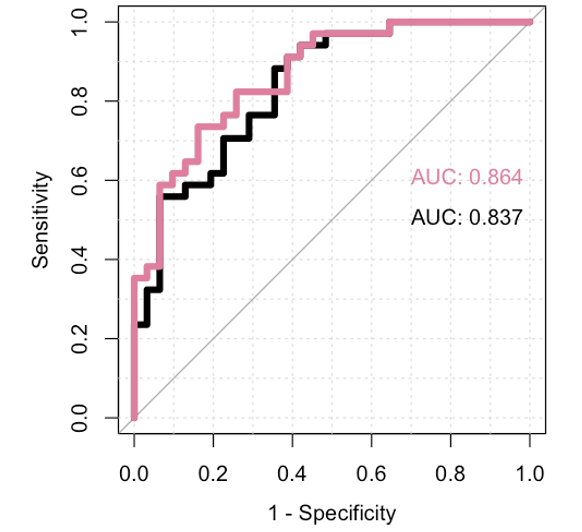
The AUC for BPD prediction using the 5 proteins with higher fold-change in NPA from the proteomic analysis was 0.78; when four clinical variables were added (CRIB-II score, hemodynamically significant persistent ductus arteriosus at 7 days, intubation in the delivery room and need of surfactant) this AUC increased to 0.82; if LU score was included in the final model, the AUC reached 0.86.
Conclusion(s): In this big sample of infants born before 30 weeks from different centers, the use of proteomic analysis from NPA and lung ultrasound at seven days of life, increase the early diagnostic accuracy of clinical variables.