Immunizations/Delivery
Session: Immunizations/Delivery 2
50 - Standing Orders to Assist with HPV Vaccination Workflow: Perspectives from Pediatric and Family Medicine Personnel
Saturday, May 4, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 50
Publication Number: 50.1424
Publication Number: 50.1424

Cynthia M. Rand, MD, MPH (she/her/hers)
Professor Pediatrics
University of Rochester
ROCHESTER, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: HPV-related cancers impact ≥21,000 women and 15,000 men annually in the U.S. Despite high HPV vaccine effectiveness, uptake remains low, with only 62% of 13-17 year olds up-to-date (UTD). Strategies to increase HPV vaccination rates, including workflow optimization, are needed. Use of standing orders (SOs) to increase HPV vaccine uptake has had varying outcomes, and a better understanding of factors related to SOs success is needed.
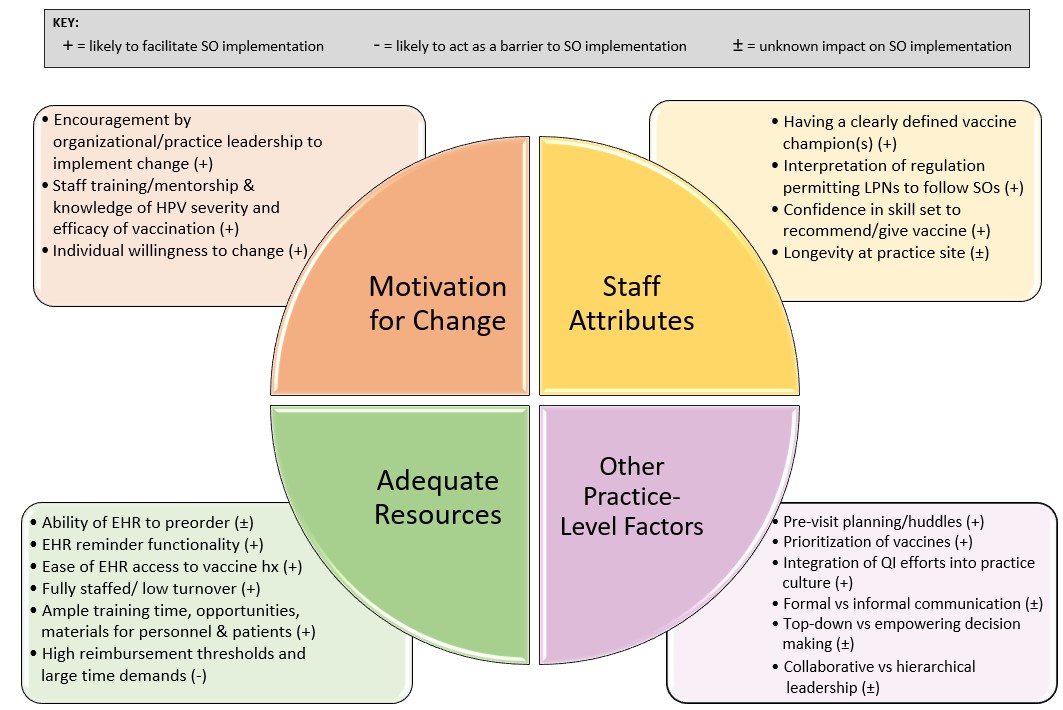
Objective: Apply the Organizational Readiness for Change (ORC) model to assess factors related to the feasibility of implementing SOs. The four ORC domains assessed included: motivation to change, adequate resources, staff attributes, and other practice factors.
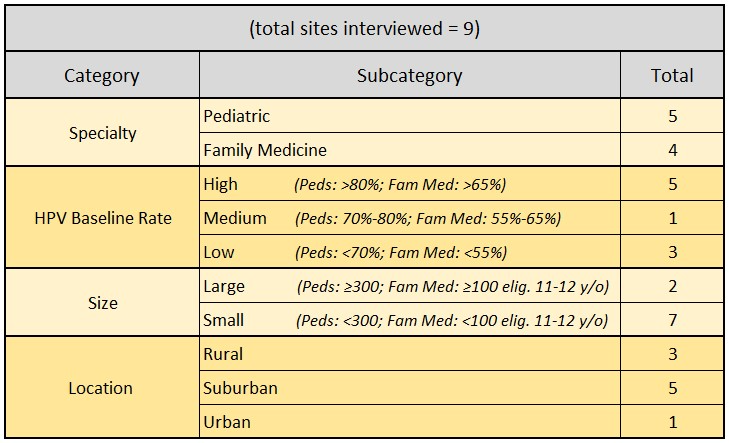
Design/Methods: We conducted interviews with clinical personnel from pediatric and family medicine practices in Western New York, using purposeful sampling to reach practices of varied size and baseline HPV vaccination rates (Table 1). We designed the interview tool to assess practice demographics and factors that mapped onto ORC model domains. Interviews were audio recorded and transcribed. Rapid qualitative analysis was used to identify common themes. Interview summaries were consolidated into a master spreadsheet, categorized by theme, and analyzed to assess factors that may hinder or enhance use of SOs.
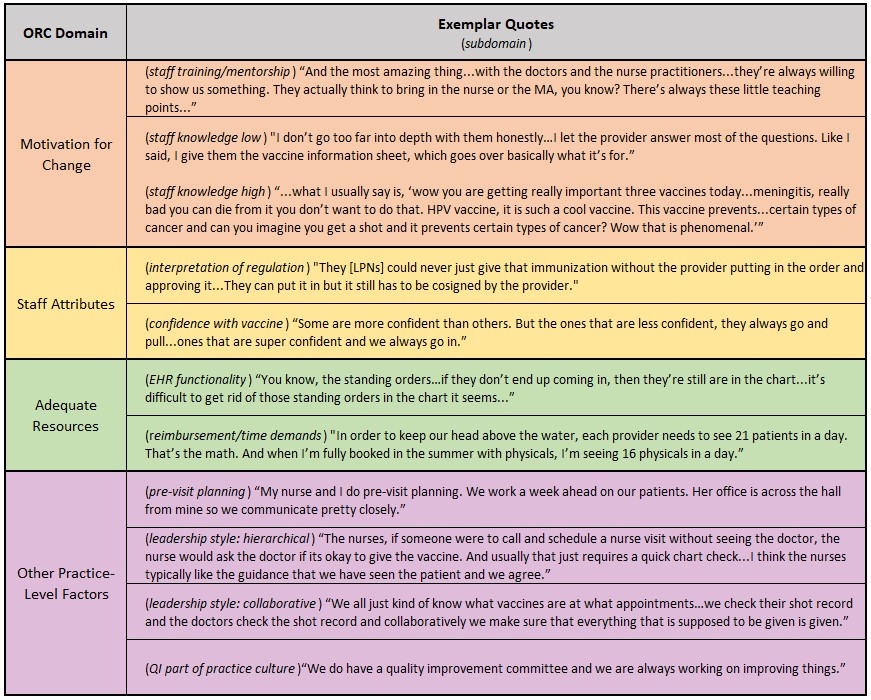
Results: Between June - October 2023, we interviewed 20 key informants (6 providers, 9 nurses, and 5 practice managers) in 9 practices (HPV vaccination UTD rates for 13-17 year olds were 35-91%). We identified factors affecting SO uptake in each ORC domain (Figure 1). In motivation for change, factors included: practice leadership support, HPV vaccine knowledge, and willingness to change. In adequate resources, EHR functionality, being fully staffed, and training time/materials facilitated uptake, while high reimbursement thresholds were a barrier. In staff attributes, facilitators included having a clearly defined vaccine champion, allowing LPNs to follow SOs, and confidence in recommending HPV vaccine. Finally, other practice-level factors influencing SO implementation included use of pre-visit planning, quality improvement history, leadership style, and communication practices. Exemplar quotes associated with select factors are shown in Table 2.
Conclusion(s): Addressing modifiable factors in each ORC domain (e.g., leadership support, EHR functionality, confidence with vaccines, pre-visit planning) could improve implementation and effectiveness of SOs as a strategy for increasing HPV vaccine uptake.