Breastfeeding/Human Milk
Session: Breastfeeding/Human Milk 3: Milk Composition
495 - Network-Based Bioinformatics Highlights Broad Importance of Human Milk Hyaluronan
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 495
Publication Number: 495.1963
Publication Number: 495.1963

Hua Zhong, Master (he/him/his)
Research Technician
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Norman, Oklahoma, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Human milk (HM) is rich in bioactive factors that promote postnatal development of the small intestine (SI) & maturation of the microbiome. HM is also protective against necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). The HM glycosaminoglycan, hyaluronan (HA), is present at high levels in colostrum & early milk. Our group demonstrated that HA 35 kDa (HA35, a HM HA mimic) is protective in two NEC models. Further, HA35 promotes maturation of the murine neonatal SI through increased villus length and crypt depth, more abundant goblet & Paneth cells, & changes in the microbiome. However, the molecular mechanisms underpinning HA35-induced changes in the Sl epithelium are unclear.
Objective: Determine if pathway & network analysis of bulk RNA-seq transcriptomics can establish mechanisms contributing to SI differentiation and maturation.
Design/Methods: Bulk RNA-seq was conducted on SI samples from postnatal day 14 in CD-1 mouse pups treated with HA35 (30 mg/kg, P7-P14, n=4) or control (n=4). Using the CORALL kit, stranded RNA-seq libraries were prepared from 200-500 ng RNA & indexed for multiplex sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000. Reads were mapped to mouse genome (mm10) using gSNAP, expression levels quantified as FPKM with Cufflinks. Differentially expressed genes underwent pathway analysis with Qiagen IPA & GSEA using the Hallmark database. Cell composition was deciphered with the granulatorSpatialDecon R package referencing the scRNA-seq Mouse Cell Atlas. PPI networks & central genes were analyzed in CytoScape with CytoHubba, ClueGo, and STRINGapp plugins.
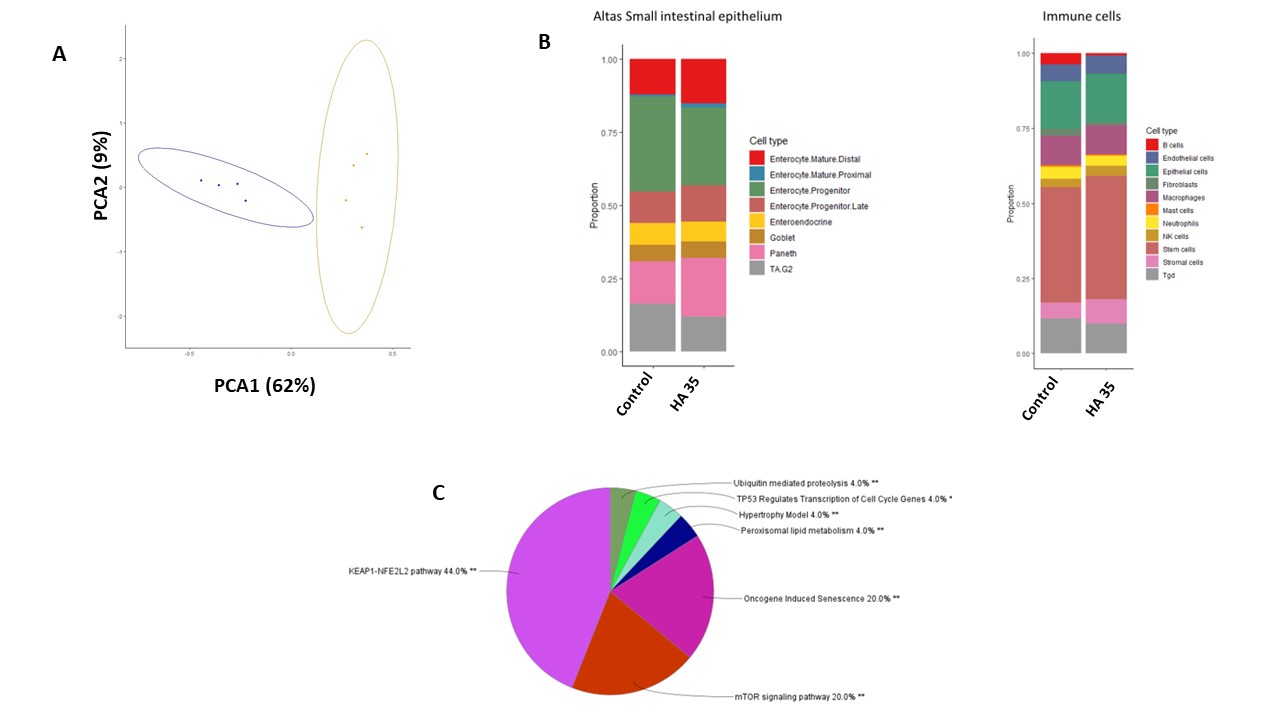
Results: HA35-treated pups distinctly separated in PCA clustering (Fig1A).247 DEGs were observed with 200 upregulated and 47 downregulated in HA35-treated pups against controls. Key upregulated pathways included 14-3-3-mediated, EIF2, ERK/MAPK, HIF-1α, mTOR, PI3K/AKT, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), VEGF, IGF-1, & NRF2-mediated oxidative stress response, while apoptosis and PPAR signaling were downregulated.GSEA showed associations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition, MYC targets, and G2M checkpoint. Cell deconvolution indicated increased Paneth cells, stem cells, & other specific cell types (Fig1B). Notably, pathways like KEAP1-NFE2L2, mTOR, & TP53 regulation were identified (Fig1C).
Conclusion(s): The observed upregulation of pathways associated with cellular growth, differentiation, & response to stress, coupled with the downregulation of apoptosis &inflammatory signaling, underscores HA35's potential as a HM bioactive factor that protects against NEC. Further confirmation of the findings is ongoing in human preterm enteroid models.