Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Nephrology/AKI 1
37 - Identification of a Shorter Time Period for Neonatal Urine Output Monitoring
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 37
Publication Number: 37.1882
Publication Number: 37.1882

Jennifer L. Chmielewski, MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatology Fellow
Indiana University School of Medicine
Westfield, Indiana, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Accurate determination of neonatal urine output is essential and is classically evaluated over the course of 24 hours. Identification of a shorter time interval for urine output collection that reflects clinically significant urine output may allow for easier recognition of low urine output.
Objective: To identify the minimum time interval reflective of 24-hour neonatal urine output via comparison of mean urine output over 6 hours, 12 hours, and 24 hours in critically ill neonates from day of life (DOL) 2 through DOL 7.
Design/Methods: Retrospective single-center de-identified cohort study of neonates admitted to a level III neonatal intensive care unit from January-August 2023. Inclusion criteria: neonates with electronic health record (EHR) documentation of at least 6 weighted diapers or urinary catheter in place per 24-hour period including at least (1) 24-hour period, between DOL 2-7. Urine output data from DOL 2-7 was collected. The lowest mean urine output over a 24-hour period from DOL 2-7 was used for each patient. Mean urine output (ml/kg/hr) was analyzed in 6-hour and 12-hour increments and compared to the mean urine output over that same 24-hour interval for each patient. Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test analysis was used to evaluate difference in median urine output between time intervals. Bland-Altman plots were used to evaluate the agreement of mean urine output between time intervals.
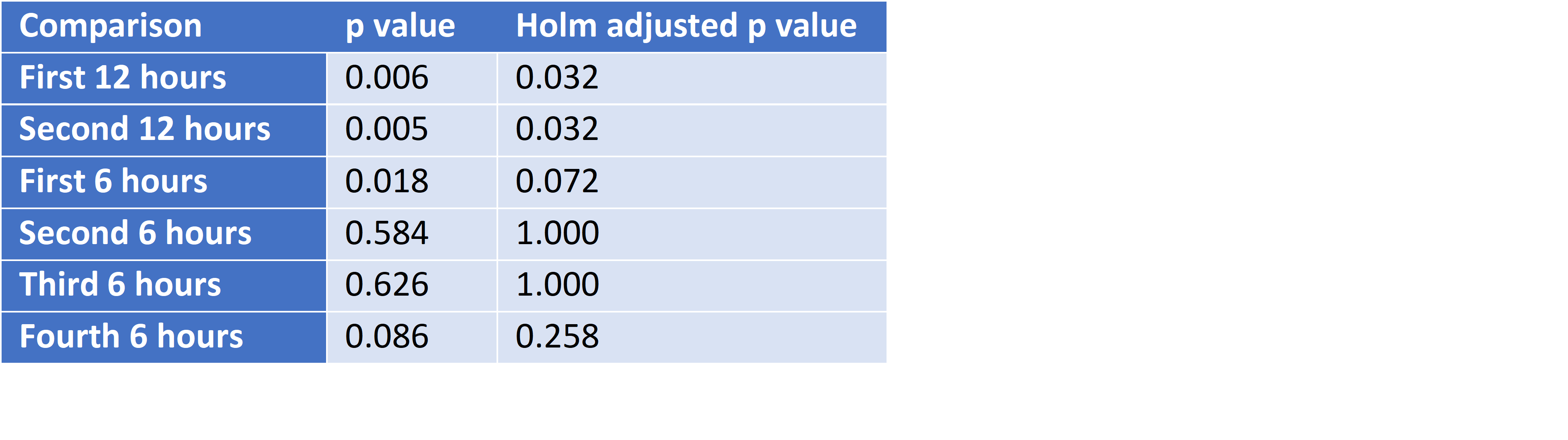
Results: Of 488 eligible patients, 200 neonates were included in the analysis, after 288 neonates were excluded due to insufficient weighted diapers, death or discharge prior to DOL 2, or admission after DOL 7. Median 6-hour urine output did not differ from the 24-hour output (p=0.072-1.000). 12-hour output differed from the 24-hour output (p=0.032, Table 1). Bland-Altman plots showed Limits of Agreement up to ±2 mg/kg/hr when comparing 6- and 24-hour periods and up to ±1.4 ml/kg/hr when comparing 12- and 24-hour urine output measures (Table 2).
Conclusion(s): Mean urine output over 6 hours and 12 hours does not reflect 24-hour mean urine output. To determine clinically important changes in urine output, it may be necessary to evaluate a neonate's urine output over 24 hours and shorter time periods may not be clinically useful.