Quality Improvement/Patient Safety
Session: Quality Improvement/Patient Safety 4
30 - Using Lean Methodology to Improve Time to Antibiotics in Febrile Immunocompromised Pediatric Emergency Department Patients
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 30
Publication Number: 30.3184
Publication Number: 30.3184

Jenna L. Spencer, DNP, APRN, ACCNS-P, CPEN (she/her/hers)
Clinical Nurse Specialist
Johns Hopkins Children's Center
Baltimore, Maryland, United States
Presenting Author(s)
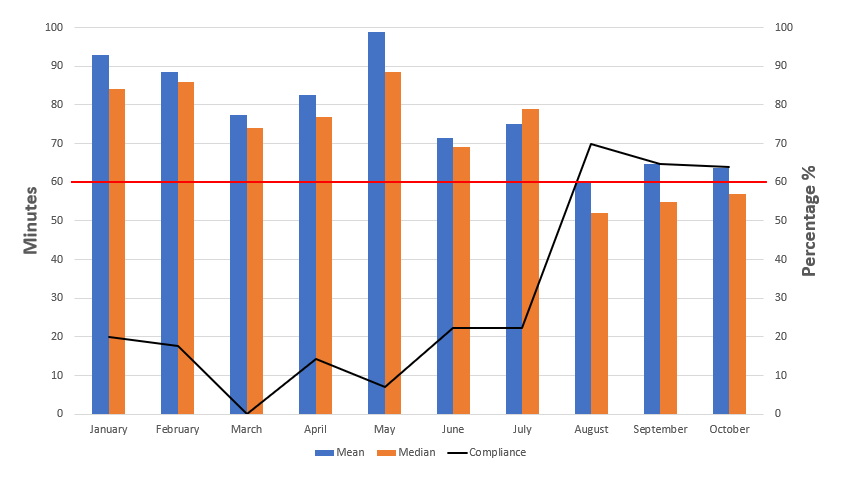
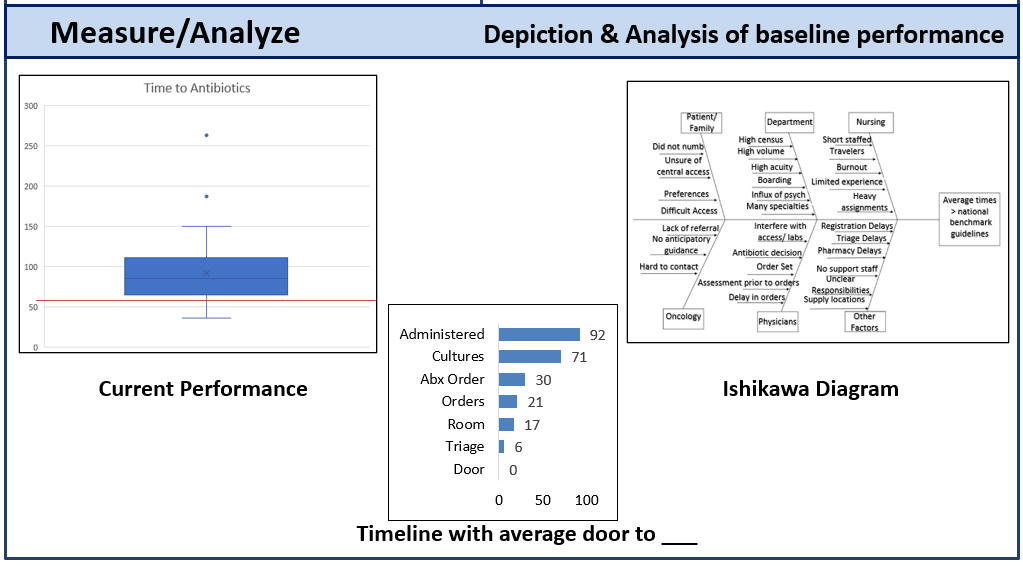
Background: Febrile Neutropenia is the most common, life-threatening oncologic emergency with significant morbidity and mortality. When an immunocompromised patient encounters an infectious pathogen, they have limited ability to fight off the infection; therefore, risk of sepsis is significantly higher. Prophylactic antibiotics at the onset of fever and neutropenia (F&N) can decrease bloodstream infection events in high-risk patients. Prompt empiric antibiotic therapy has drastically improved outcomes and decreased mortality from febrile neutropenia. The average time from arrival to the Pediatric Emergency Department (PED) to prophylactic antibiotic administration in febrile immunocompromised patients at the XX was well above the national benchmark of 60 minutes.
Objective: The objectives were to reduce the average time from arrival to antibiotic administration in febrile immunocompromised oncology patients to less than 60 minutes and increase the percentage of patients who are compliant with the 60-minute time frame.
Design/Methods: Using Lean tools and templates, including an A3, Value Stream Mapping, Sequence of Events, Spaghetti Diagram, Voice of Customer, 5 Whys, SIPOC Diagram, 7 Wastes table, Intervention PICK chart, and Control Plans, we analyzed the inefficient systems encountered and used mistake-proofing to target specific metrics within each step of the process. The interventions selected were also from evidence-based systematic reviews that were proven beneficial in like institutions.
Results: These iterations resulted in a statistically significant decrease in time to antibiotics that complied with national guidelines in addition to increasing the compliance by over 50%.
Conclusion(s): Lean Methodology is a beneficial framework for addressing multidisciplinary deficiencies in an environment with many co-existing systems. The voice of the front line is extremely valuable in driving the necessary changes to ensure high-quality care is delivered to prevent worsening morbidity and mortality of vulnerable patients.
.png)