Critical Care
Session: Critical Care 2
128 - Onco-Critical Care Collaborative- Enhancing Care of Oncology and Bone Marrow Transplant Recipients in the Pediatric ICU: Early Learnings and Interventions
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 128
Publication Number: 128.2960
Publication Number: 128.2960
- SP
Sue Poynter, MD, MEd (she/her/hers)
Professor of Clinical Pediatrics
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Children with cancer and/or undergoing bone marrow transplantation (BMT) make up a significant portion of the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) patient population. These patients require a high degree of specialized care and collaboration between critical care and oncology/BMT teams. In response to this need, we created a cross-divisional collaborative.
Objective: This initiative aims to identify targets for enhancing patient care, assess the adequacy of resources, evaluate the support systems for patients and families, and collect recommendations for the continued improvement of care.
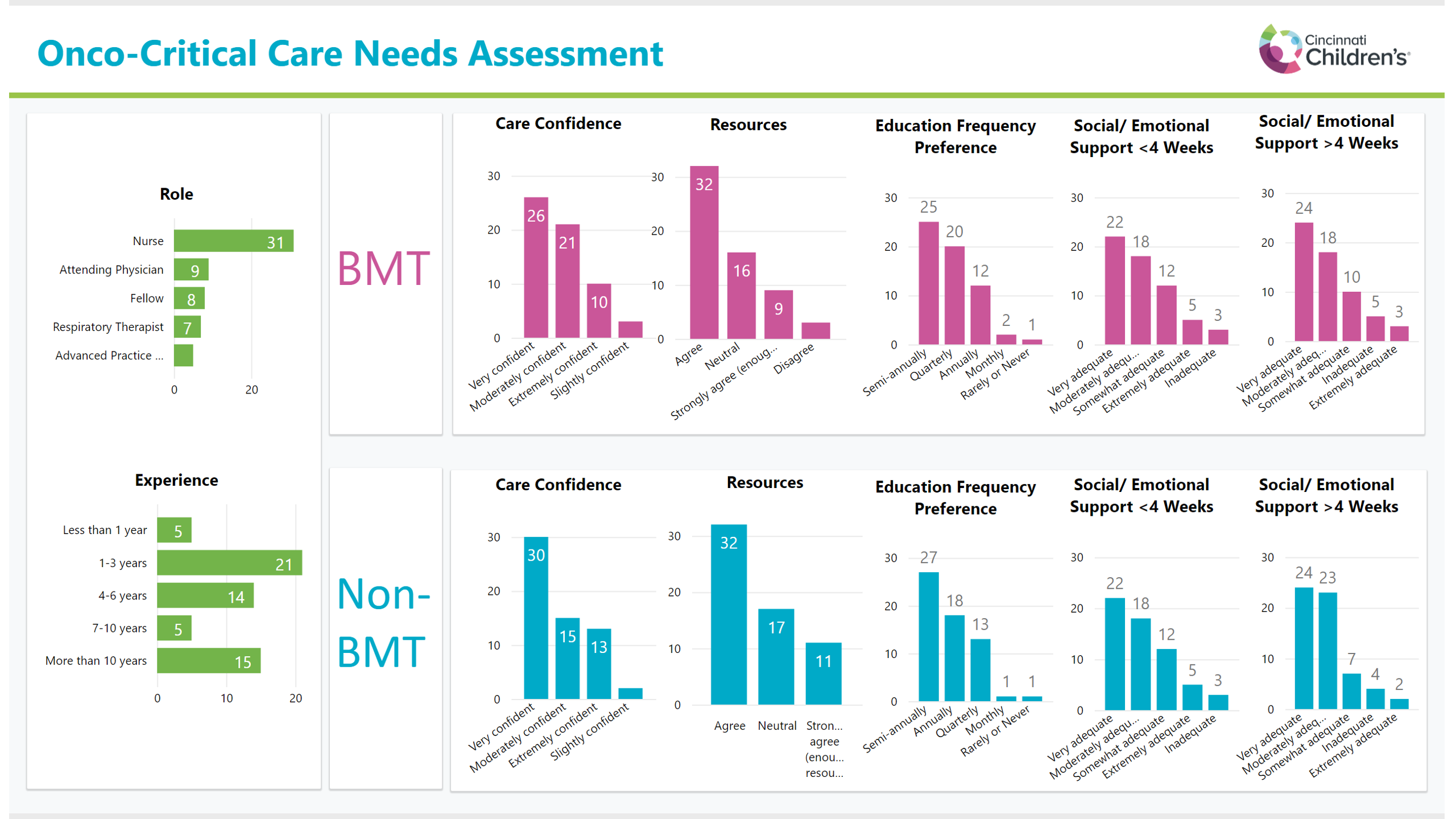
Design/Methods: We utilized the Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (KSA) framework to create a structured survey to gather baseline data on staff experience, support, confidence, educational preferences, and challenges and rewards, in caring for oncology/BMT patients. Subsequently, the findings from these structured surveys were leveraged to implement early interventions aimed at enhancing care delivery and training.
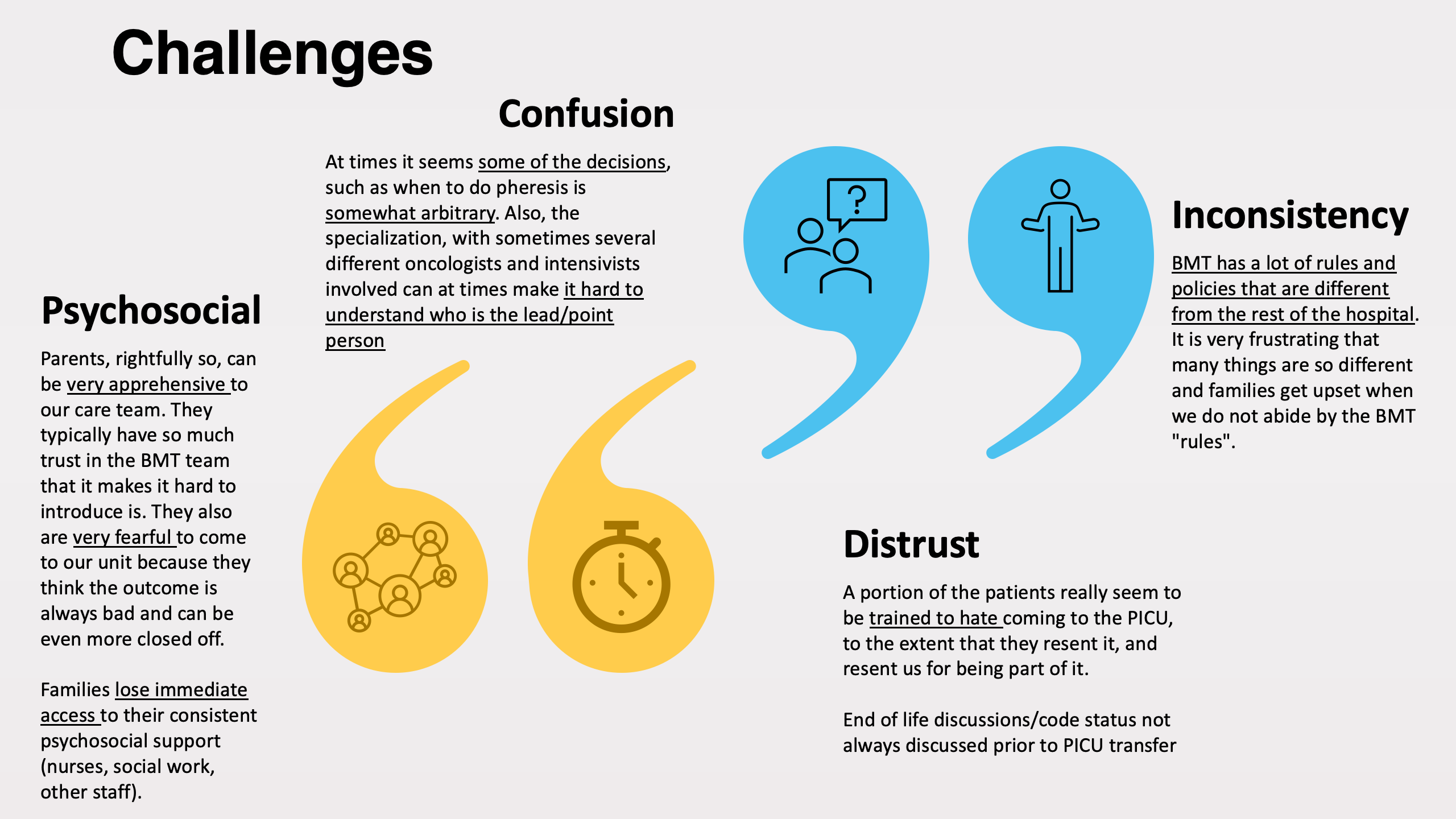
Results: 60 PICU providers were surveyed, including RTs, RNs, MDs, APNs all ranging from novices to seasoned professionals with >10 years of experience. Most respondents displayed at least a "moderate" level of confidence in caring for oncology/BMT patients. Many shared that the families posed both the most rewarding but also the most challenging aspect of care, highlighting a unique challenge in caring for these patients. Providers were satisfied with the adequacy of resources but frustrated at the lack of standardization of care of patients. Participants preferred semi-annual or quarterly oncology and BMT specific education and training.
This cross-divisional collaborative initiative has yielded unique educational opportunities, including simulation-based training and an onco-critical care training month. This collaborative has facilitated early cross-divisional care standardization while accelerating training through targeted improvement initiatives.
Conclusion(s): This cross-divisional collaborative has identified target areas to improve care for pediatric oncology/BMT patients in the PICU, including increased training and standardization of care. Collaborative training, specifically diagnosis-specific simulation and the advent of an onco-critical care training month, is a promising avenue to improve patient care. Development of clinical pathways for cross-divisional care standardization are ongoing. These early learnings and interventions provide a foundation for future developments in onco-critical care and may serve as a model for future cross divisional collaboratives beyond onco-critical care.