Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Quality Improvement 3
414 - Early Onset Sepsis Risk Evaluation and Management of Infants Born at 34 Weeks: a QI Project
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 414
Publication Number: 414.2176
Publication Number: 414.2176

Alexandra Iacob, MD, MPH
Neonatologist
MemorialCare Miller Children's & Women's Hospital Long Beach
Long Beach, California, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Infants born 34w0d-34w6d represent a significant portion of preterm admissions to NICUs. AAP recommends using delivery indications and infant’s presentation as the main deciding factors for empiric antibiotic decisions for infants born at this gestation. Conversely, the Kaiser Early Onset Sepsis (EOS) Calculator takes maternal factors and infant’s presentation to determine blood culture and empiric antibiotics management. Our unit’s heterogenous approach to EOS evaluation and management of infants born 34w0d-34w6d led to this QI project.
Objective: Our objectives include:
1) Standardize EOS management among 34w0d-34w6d infants.
2) Assess adherence to unit EOS guidelines.
3) Assess antibiotic use and blood culture management under new guidelines.
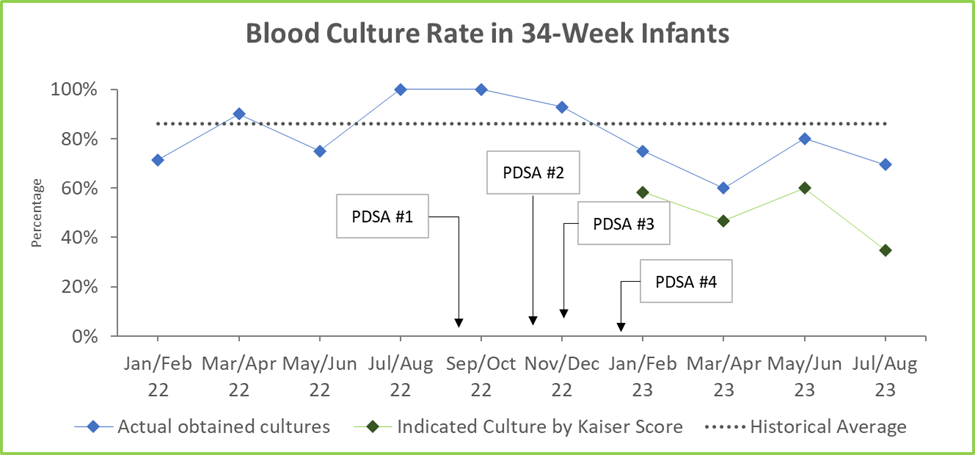
Design/Methods: The QI work is set in a 96-bed level IV NICU within an urban hospital. Participants include NICU nurses, hospitalists, and neonatologists. The first PDSA cycle included chart review of infants born at 34w0d-34w6d in 2022 to review the unit’s EOS management. The second PDSA cycle included literature review and development of a unified approach to EOS management from input and consensus of the neonatologists. In the third PDSA cycle, the use of an EOS guideline based on Kaiser EOS score to decide on antibiotic and blood culture management was tested. The most recent PDSA cycle involved the education of NICU and L&D nurses on the new unit guideline.
Results: Chart review revealed a heterogenous EOS approach for infants born at 34w0d-34w6d in 2022 (n=76) with 42% managed per AAP guidelines, 36% per Kaiser guidelines, and 22% with no guidelines documented. 2022 baseline antibiotic usage rate was 46%. During PDSA cycle 2, 12 out of 15 physicians completed our survey with majority opting to use Kaiser EOS Calculator. Since the introduction of the Kaiser EOS score in December 2022, 60 infants born at 34w0d-34w6d have been admitted. The EOS score was documented in 51 infants (85% adherence). Blood cultures were obtained in 45 infants, of which 17 were unnecessary per EOS scores. A total of 21 infants (35% antibiotic usage rate) received antibiotics, of which 4 did not meet criteria per EOS score (see Fig 1 and 2). Our balancing measures reveal that 1 infant had a positive blood culture, which was captured by an elevated EOS score. No infant required additional septic workup during the first 3 days of life.
Conclusion(s): Implementation of a standardized EOS management guideline for infants of 34w0d-34w6d gestation has led to a unified approach with a decrease in usage of antibiotics from 46% to 35% across an 8-month timeline, without any adverse effects.
.png)
