Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Quality Improvement 6
94 - Reducing Healthcare-Associated Respiratory Infection Rates in a Level IV Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 94
Publication Number: 94.2801
Publication Number: 94.2801
.jpg)
Lydia Schneider, MD (she/her/hers)
Pediatric Resident Physician
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago
Chicago, Illinois, United States
Presenting Author(s)
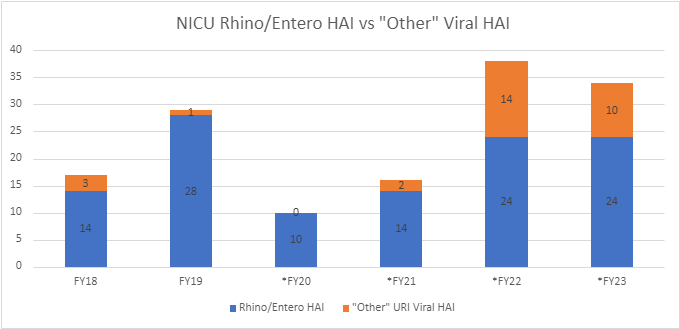
Background: The healthcare-associated respiratory virus rate at Lurie Children’s Hospital increased significantly between fiscal year (FY) 2021 and 2022. Among these healthcare-associated infections (HAI), 56% were rhino/enterovirus infections, with clusters reported in the critical care setting. Despite universal masking of healthcare workers (HCW), the number of rhino/enterovirus HAIs in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) from FY2021 to FY2022 increased 64% due to barriers with isolation precautions, hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), and visitor contacts.
Objective: The objective was to decrease the number of healthcare-associated rhino/enterovirus and total respiratory viral infections in a level IV NICU in FY2023.
Design/Methods: Opportunities to improve isolation and PPE compliance of NICU patients with unique clinical scenarios were identified. A PPE algorithm for respiratory viruses was created to streamline isolation precautions of NICU patients under investigation (compatible symptoms and/or pending test result) and with confirmed infection. With the introduction of universal masking, the steps for doffing were updated to reflect an individual’s need to replace his or her mask under any type of droplet isolation upon exit. “Replace Mask” signage was designed to raise awareness of this policy change, along with a nursing documentation bundle to improve screening, isolation, and education compliance. Family fliers were developed in English and Spanish to encourage visitor and community engagement.
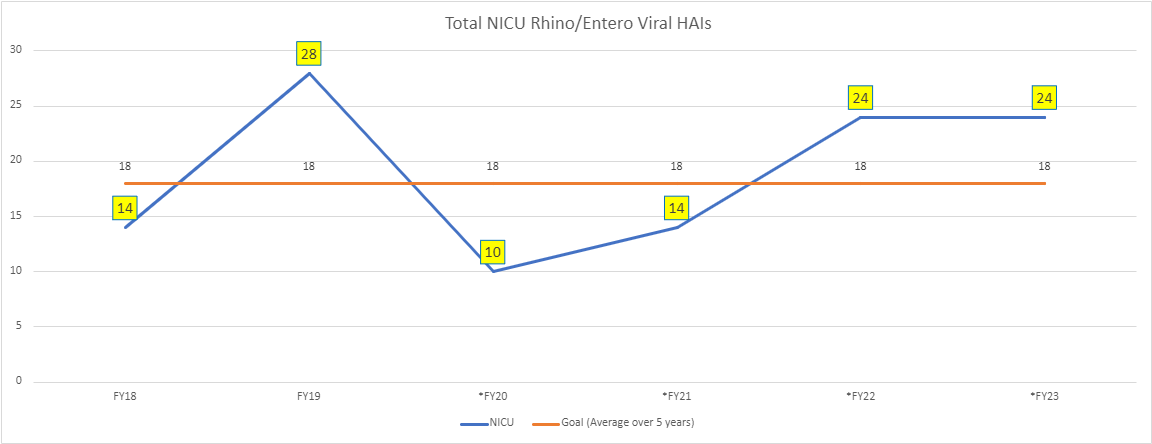
Results: The PPE algorithm and “Replace Mask” signage continue to be utilized for patients with suspected and confirmed respiratory viral infections. Mask surveillance, where Infection Prevention and Control (IP&C) audits individuals exiting patient rooms on droplet isolation for mask replacement, improved from 25% (pre-intervention) to 70% (as of December 2022). Patients that acquire rhino/enterovirus undergo IP&C chart audits, with a 67% bundle compliance rate since process implementation. The number of rhino/enterovirus infections was unchanged from FY2022 to FY2023, but total respiratory infections decreased by 10.5% post-intervention (Figures 1-2).
Conclusion(s): These results suggest that the PPE algorithm, “Replace Mask” signage, and nursing documentation bundle improve isolation and PPE compliance of HCWs, in addition to providing updated steps to doffing with universal masking in place. While NICU rhino/enterovirus HAIs continue, prevention efforts are ongoing with IP&C, HCWs, families, and staff.