Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Neurology 8: Preclinical
326 - Long-lasting enhanced neuroprotective effect by combining URB447 and therapeutic hypothermia after hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 326
Publication Number: 326.3069
Publication Number: 326.3069
- MC
Marc Chillida, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
PhD Student
University of the Basque Country
Bilbao, Pais Vasco, Spain
Presenting Author(s)
Background: During the perinatal period, neonatal hypoxia-ischemia (HI) may cause hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. These newborns may develop life-long neurological disabilities or even die. Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) is the standard treatment used in clinics; however, nearly half of the babies treated still die or survive with disability despite cooling, hence, combined therapies are urgently needed.
Objective: The aim of this work was to assess the long-term neuroprotective effect of the administration of the synthetic cannabinoid URB447 in combination with TH using a preclinical model of HI in neonatal rats.
Design/Methods: Seven-day-old Sprague Dawley rats underwent HI (8% oxygen for 120 min after left-common carotid artery electrocoagulation). After HI, rat pups received a single i.p. dose of 1mg/kg of URB447 or/and TH (32.5-33ºC for 3h). The resulting groups were: i) Sham (without HI, n=8), ii) HI+TH (n=24), and iii) HI+TH+URB447 (n=21). A set of animals was evaluated at P14 (short-term) to analyze the number of cortical and hippocampal mature neurons (NeuN). A second set of pups was studied by rotarod and T-maze behavioral tests on postnatal days 42 and 90. These rats were sacrificed at P90 and their brains were removed and sectioned for histological analysis: neurodegeneration was assessed by obtaining a global and regional neuropathological score and by measuring hemispheric and hippocampal infarcted areas. A p< 0.05 was considered significant.
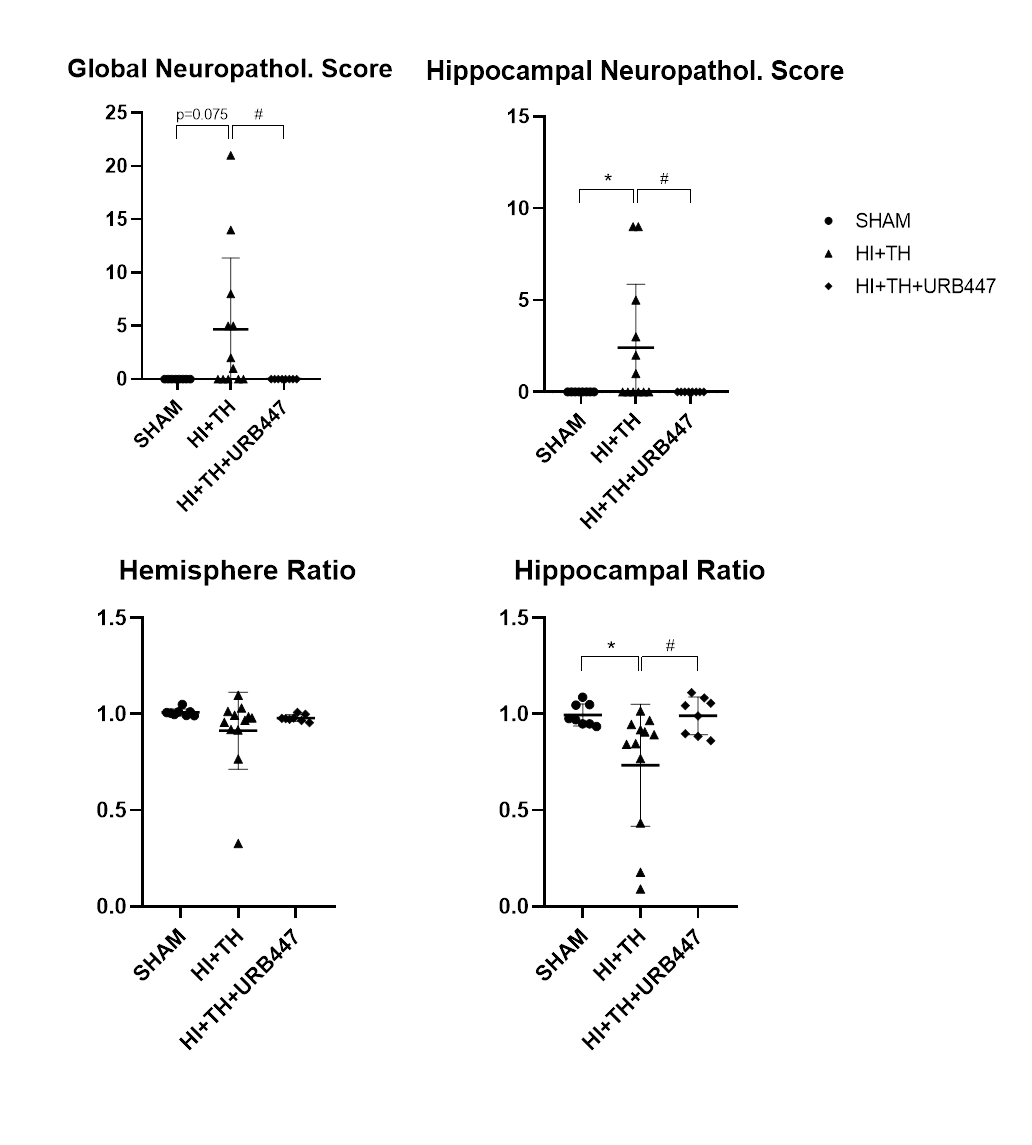
Results: At P14, the HI+TH group showed lower NeuN counts in cortex and hippocampus when compared to HI+TH+URB447 (p < 0.0001). In the behavioral tests, animals receiving the combination therapy obtained the best results (n.s. vs Sham). This beneficial effect was further confirmed in histopathological examinations: global and regional neuropathological scores for the HI+TH+URB447 were 0, whereas hypothermia-only animals showed signs of neurodegeneration (HI+TH score values: 4.6 for global and 2.4 for hippocampus). Hippocampal ratios from only-cooled pups were significantly lower (p < 0.05) than those from Sham; this was resolved by the combined therapy HI+TH+URB447, with higher ratios than cooling alone (p < 0.05) and similar to Sham, revealing minor signs of brain injury.
Conclusion(s): These results suggest that the synthetic cannabinoid URB447 enhances the neuroprotective effect of TH after HI in neonatal rats, a beneficial effect that was long-lasting.
Acknowledgments: Grant MINECOR20/P66 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by “ERDF A way of making Europe”, UPV/EHU predoctoral grant (PIFBUR22/03).