Neonatology
Session: Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 1
266 - Optimal Endotracheal Tube Tip-to-Gum Depth in Very Low Birth Weight infants
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 266
Publication Number: 266.2994
Publication Number: 266.2994
- RG
Ruby Gupta, MD MS (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor
Medical College of Wisconsin
MCW
Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Proper placement of the endotracheal tube (ETT) in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants is crucial for providing adequate ventilation and minimizing complications. The American Academy of Pediatrics Neonatal Resuscitation Program (AAP-NRP) states the ideal position for the ETT tip is within the upper border of the first thoracic vertebra (UB T1) and the lower border of the second thoracic vertebra (LB T2). Various methods have been proposed to calculate the optimal depth for ETT placement, but these rely on the position of the lips which can lead to inaccuracy in ETT placement. The upper gum may represent a more stable and reliable anatomical landmark for assessing ETT depth.
Objective: To determine the optimal ETT tip depth from the gum (Tip-to-Gum) relative to birth weight (BW) and gestational age (GA) and compare it to the AAP-NRP’s Tip-to-Lip
Design/Methods: This is a retrospective study of VLBW ( < 1500 gms) and < 32 weeks GA, intubated in the delivery room (DR) and admitted to a Level IV NICU from 1/2021–2/2022. ETT depth was measured Tip-to-Gum and documented before imaging. To enhance the visibility of chest X-ray (CXR) structures, we used Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE). Precise measurements from UB T1 to the ETT tip and from LB T2 to the ETT tip were taken using electronic calipers. Two neonatologists independently conducted measurements to ensure consistent positioning. Utilizing polynomial regression, we modeled the optimal ETT placement between the UB T1 and the LB T2, correlating it with GA and BW.
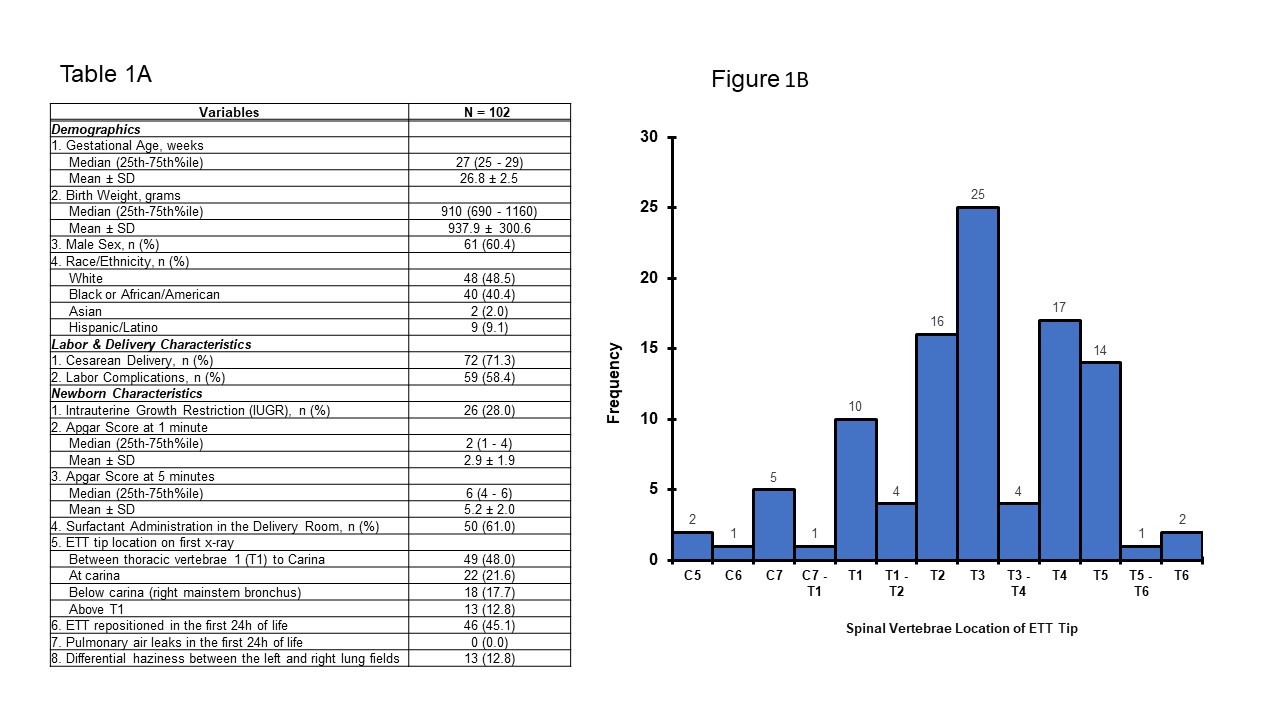
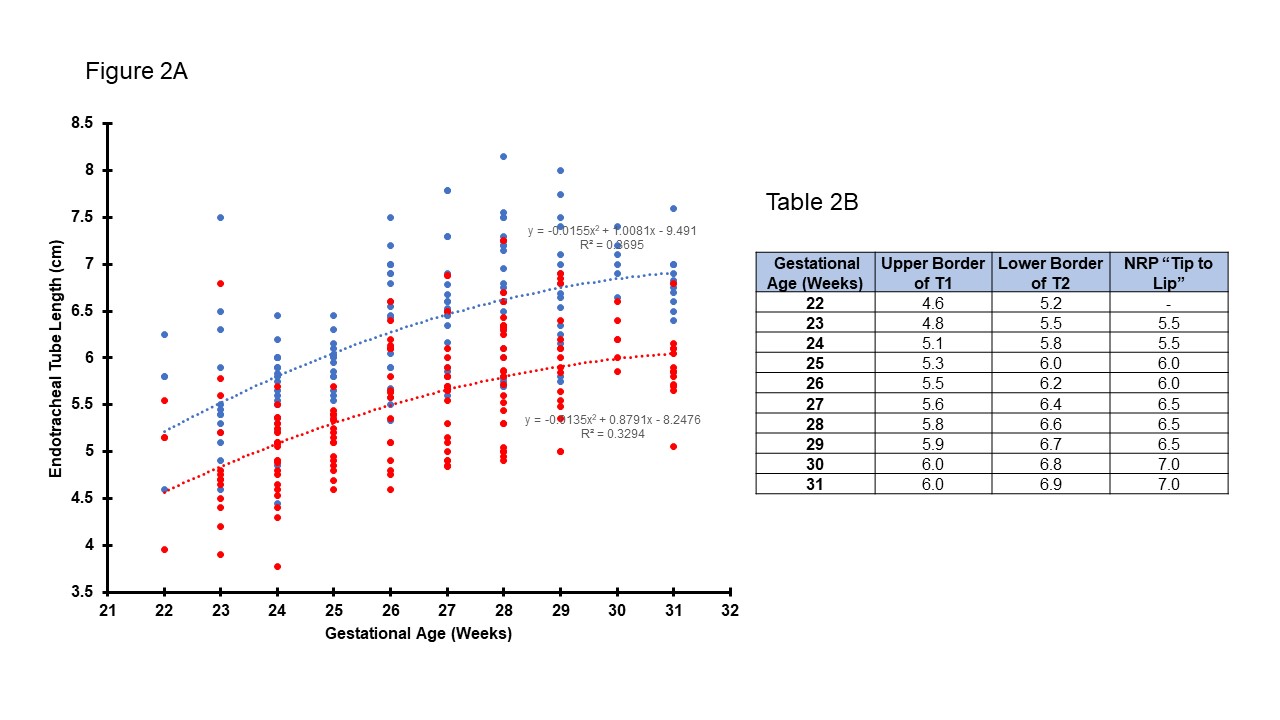
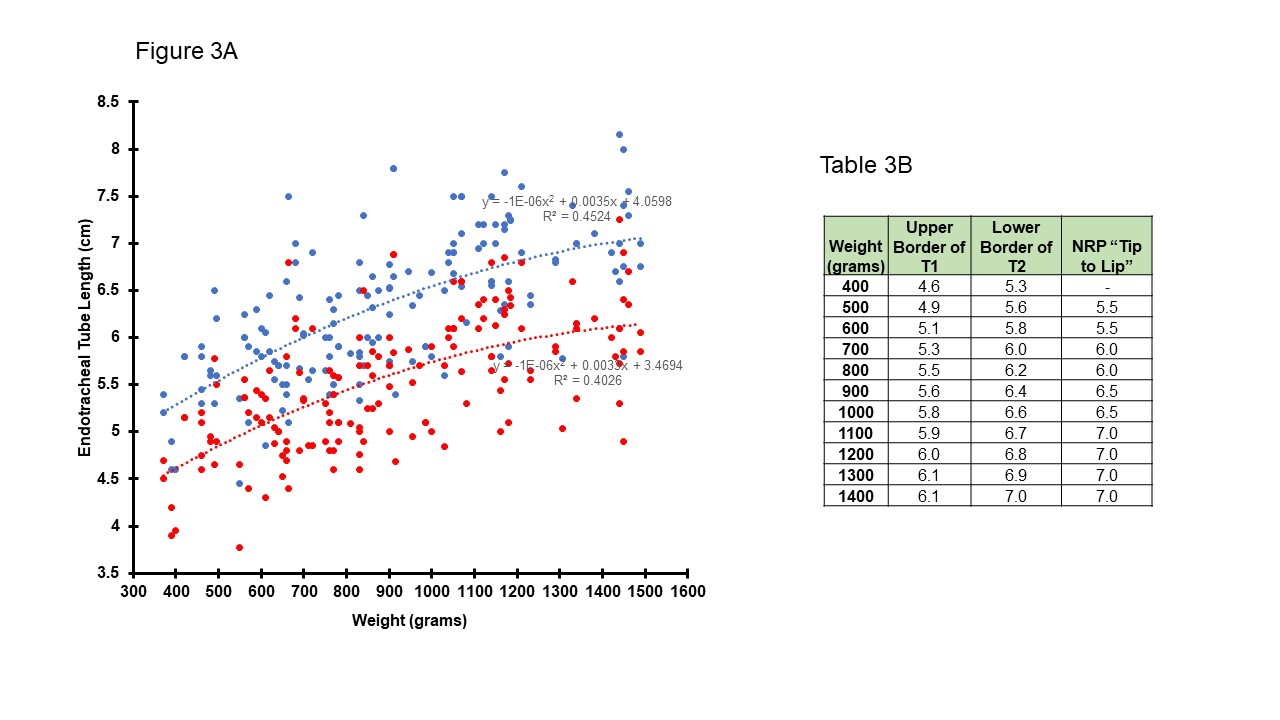
Results: Out of 266 infants, 102 (38%) were intubated in the DR. The median GA was 27 weeks, and the mean BW was 938 gms, Table 1A. For first CXR, only 29% had the ETT tip between UB T1 to LB T2, and most were at T3 (25%), Fig 1B. There were 51% of infants with inappropriately placed ETT tips, and 45% needed ETT repositioning in the first 24 hrs. Fig. 2A, 3A show the optimal Tip-to-Gum depth range between the UB T1 and the LB T2. There is a consistent increase in distance from 7- 9mm in correlation with increasing GA and BW. The AAP-NRP Tip-to-Lip measurements were found to nearly mirror the Tip-to-Gum LB T2 measurements for both GA and BW, Tables 2B, 3B.
Conclusion(s): This study validates the Tip-to-Gum method as it nearly mirrors the AAP-NRP Tip-to-Lip measurements at the LB T2. By adopting the Tip-to-Gum approach, we anticipate enhanced precision in ETT placements, potentially reducing the need for adjustments. We speculate that AAP-NRP optimal ETT depth measurement Tip-to-Lip need to be decrease by around 4 mm to convert it to Tip-to-Gum measurement.