Emergency Medicine
Session: Emergency Medicine 5: Sepsis
120 - Improving sepsis recognition tools in a pediatric emergency department: A Qualitative improvement Initiative
Saturday, May 4, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 120
Publication Number: 120.1673
Publication Number: 120.1673

Leslie A. Hueschen, MD (she/her/hers)
Pediatric Emergency Medicine Physician
University of Missouri-Kansas City;Children's Mercy Hospital
KANSAS CITY, Missouri, United States
Presenting Author(s)
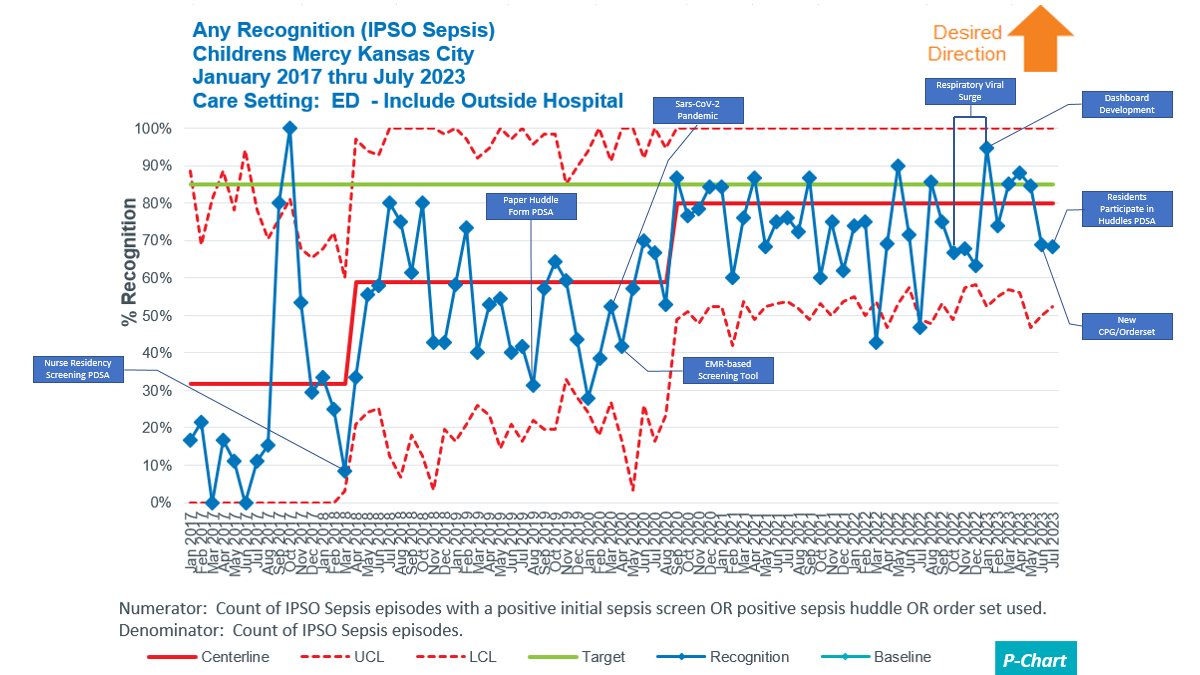
Background: The Children’s Hospital Association’s Improving Pediatric Sepsis Outcomes(IPSO) collaboration identified a reduction in sepsis-attributable mortality by utilizing a sepsis bundle of care. Bundle compliance includes receiving a fluid bolus in < 1 hour, antibiotics in < 3 hours, and utilization of a sepsis recognition tool (sepsis screen, huddle or order set). Early data demonstrates that using of a sepsis recognition tool, in itself, decreases sepsis morality. In 2017, our emergency department(ED) had a sepsis screening tool, developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics Sepsis collaboration, only performed at triage but no continuous screen. Currently only 32% of ED sepsis patients have any recognition tool used.
Objective: By July 30th, 2023, we will increase use of sepsis recognition tools from 32% to 80% in ED sepsis patients.
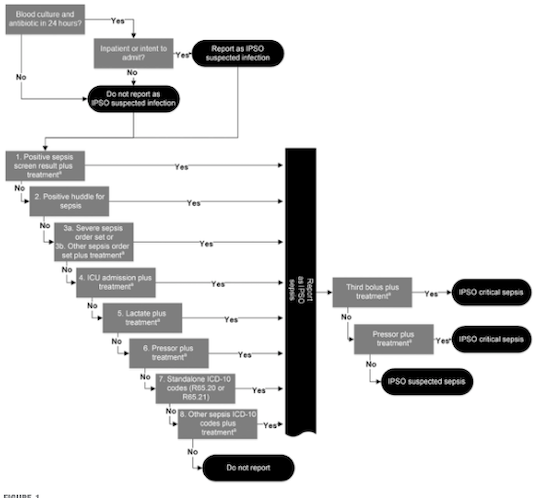
Design/Methods: ED sepsis patients included were identified by IPSO definitions.(Fig 1) Our outcome measure was 30-day sepsis-attributable mortality. Process metrics included the percentage of ED sepsis patients with bundle compliance, sepsis screen activation, and huddle. Our balance measure was sepsis incidence/1000 admissions.
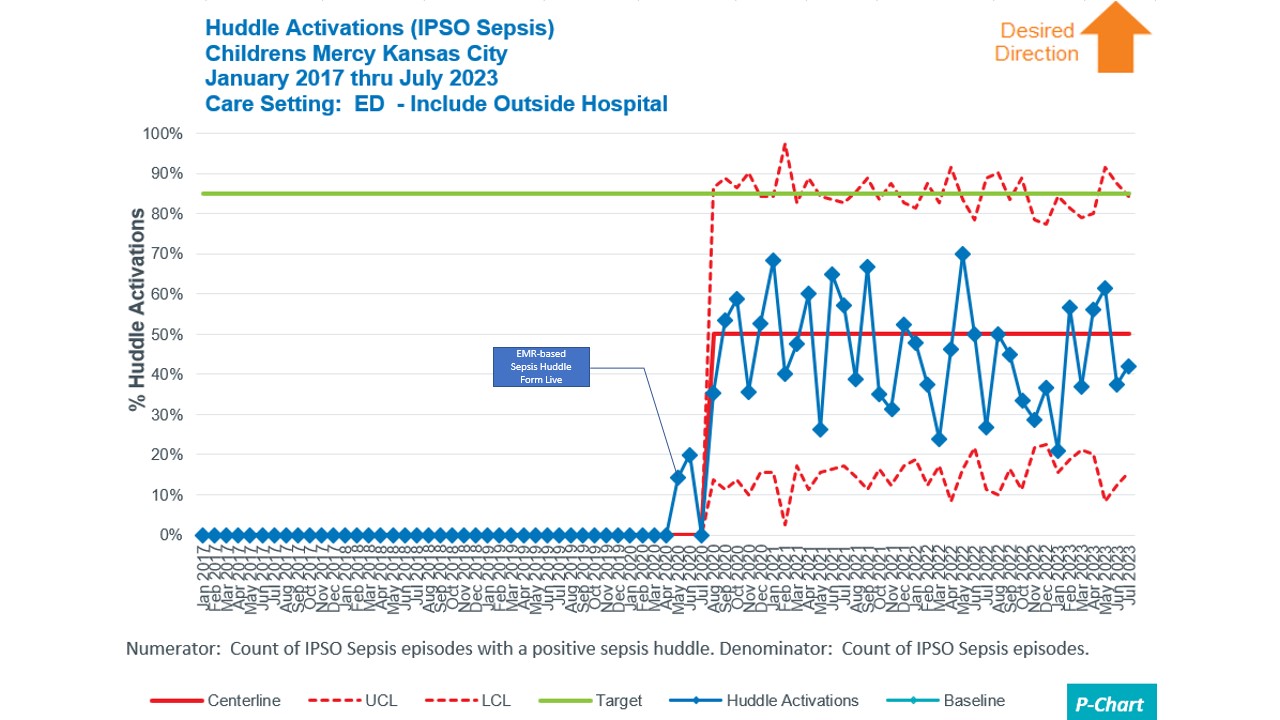
Plan-do-study-act interventions were completed. PDSA 1:(2018) Improved the nurse triage sepsis screening process with education, badge reminders, and developed internal sepsis information webpage. PDSA 2:(8/2019) Trial of a paper bedside sepsis huddle form for positive sepsis trigger patients. PDSA 3:(10/2019) Interventions to improve time to antibiotics by ordering antibiotics ‘STAT’ and bedside delivery of antibiotics by pharmacy. PDSA 4:(5/2020) Implemented an EMR-based continuous sepsis screening tool with linked electronic huddle form. PDSA 5:(1/2023) Built an ED sepsis dashboard for real time metric analysis. PDSA 6:(6/2023) We revised sepsis care process model and order set to align with new evidence-based medicine. PDSA 7:(7/2023) Included residents to be able to complete huddle form.
Results: Increases in any recognition tool(Fig 2) and huddle compliance occurred(Fig 3). Bundle compliance increased 22.6% to 46.2% in Feb 2020. 30-day sepsis-attributable mortality centerline decreased from 2.4% to 0 in Q2 2019 with increased variability. There was an increase in sepsis incidence/1000 admissions from 8.234 to 11.767 in December 2018.
Conclusion(s): Instituting an EMR cloud-based sepsis screening tool was our most impactful intervention leading to increased sepsis recognition and bundle compliance. Incidence did increase but is unlikely to be related to the new EMR screening tool because the shift occurred prior to implementation.