Neonatology
Session: Neonatal General 7: Respiratory
244 - Pulmonary Surfactant With Versus WIthout Budesonide in Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, May 6, 2024
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 244
Publication Number: 244.2961
Publication Number: 244.2961

Thaís Iwashita Lages, MD (she/her/hers)
Clinical Assistant
Hospital das Clinicas - Medical School of Ribeirao Preto - University of Sao Paulo, Brazil
Ribeirao Preto, Sao Paulo, Brazil
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia has led to the exploration of corticosteroids as anti-inflammatory agents to treat this condition. Despite numerous studies, the effectiveness of combining surfactant with budesonide in the treatment of neonatal respiratory distress (RDS) remains uncertain.
Objective: Verify the safety and efficacy of combining surfactant with budesonide in the treatment of neonatal respiratory distress.
Design/Methods: We systematically searched Pubmed, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies comparing the effectiveness of surfactant and budesonide combination therapy to surfactant-only treatment in neonates with RDS. Statistical analysis was conducted using Review Manager version 5.4, and heterogeneity was assessed through Cochrane's Q test and I2 statistics.
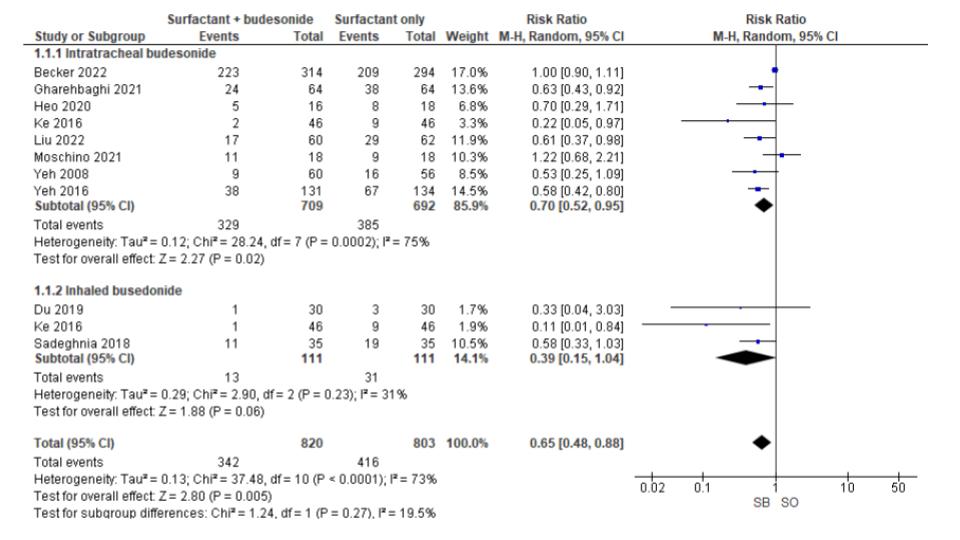
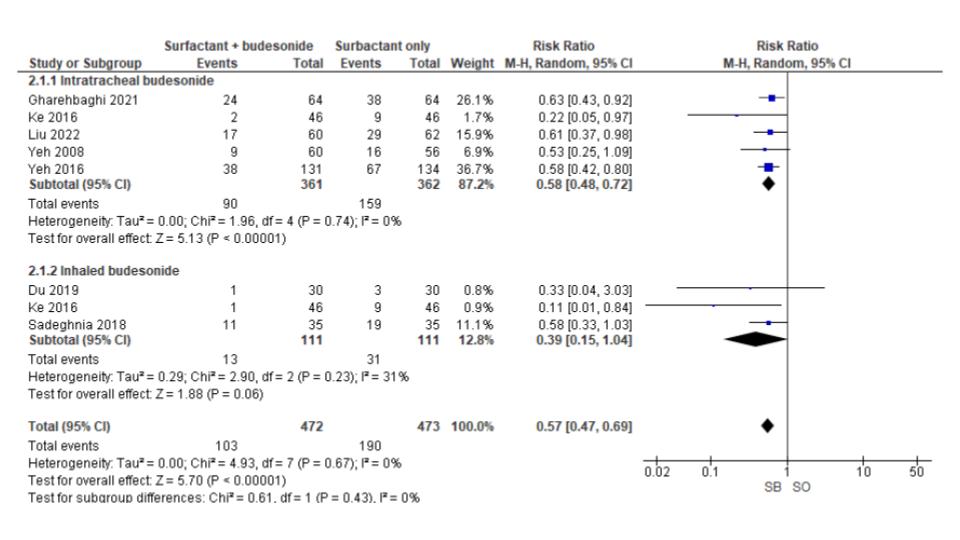
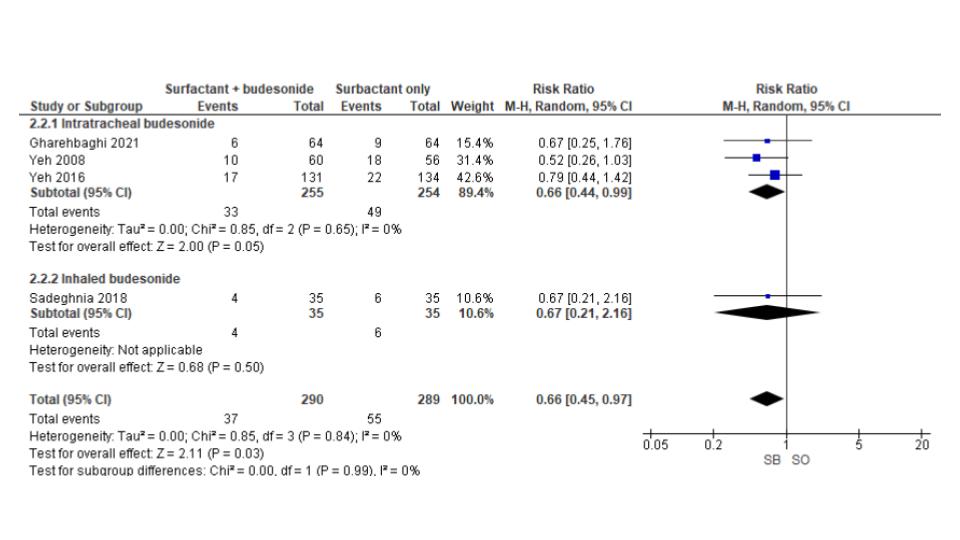
Results: We included 1577 preterm neonates from 11 studies in our analysis. Neonates treated with surfactant and budesonide had a significantly lower incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) (RR 0.65; 95% CI 0.48-0.88; p< 0.01) (Figure 1).There was no significant difference in mortality between the groups (RR 0.79; 95% CI 0.59-1.06; p=0.11). A subgroup analysis of RCTs demonstrated that surfactant and budesonide therapy was superior to surfactant-only treatment in reducing the incidence of both BPD (RR 0.57; 95% CI 0.47-0.69; p< 0.01) (Figure 2) and mortality (RR 0.66; 95% CI 0.45-0.97; p=0.03) (Figure 3).
Conclusion(s): In preterm neonates with RDS, surfactant and budesonide combination therapy significantly decreases BPD incidence compared with surfactant-only treatment. Randomized data also indicates a lower incidence of mortality in neonates treated with budesonide. These findings emphasize the potential of combined surfactant and budesonide therapy to improve outcomes in neonatal RDS.