Neonatology
Session: Neonatology Pulmonology Clinical Science 1: Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
573 - Early Airway Thrombospondin Protein Expression in ELBW infants with and without Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Saturday, May 4, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 573
Publication Number: 573.1364
Publication Number: 573.1364
- LP
Lance Parton, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
MFCH at WMC, NYMC, BCHP
Valhalla, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: BPD represents inhibition of lung development with altered lung structure, growth, and function of the distal airspaces and vasculature. Differential expression of genes in lung tissue may have important roles in BPD.
Thrombospondin-1 (TSP- 1) is an extracellular glycoprotein that has been shown to direct crosstalk between lung endothelial cells and specialized stem cells to promote differentiation into alveolar epithelial lineage-specific cells. TSP-1 counters inflammation by triggering anti- inflammatory cytokine IL-10 production in macrophages. TSP-1 knockout mice develop spontaneous noninfectious pneumonia and lung inflammation. However, to date, evidence on the role of TSP-1 in neonatal BPD is lacking.
Objective: To examine the effects of variants of the Thrombospondin-1 gene (THBS1) and early airway TSP-1 protein expression in Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) infants with and without BPD.
Design/Methods: This was a prospective observational, cohort study including ELBW infants with and without BPD. DNA was isolated from buccal swabs and subjected to RT-PCR with specific TaqMan probes for THBS1 gene variants. Airway TSP-1 protein expression was measured in tracheal aspirates collected within the first seven days subjected to ELISA. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact test was used for categorical variables. Wilcoxon Rank Sum and t-test were used for continuous variables; z-test for allele frequencies, with p< 0.05 statistically significant. The study was approved by IRB at New York Medical College.
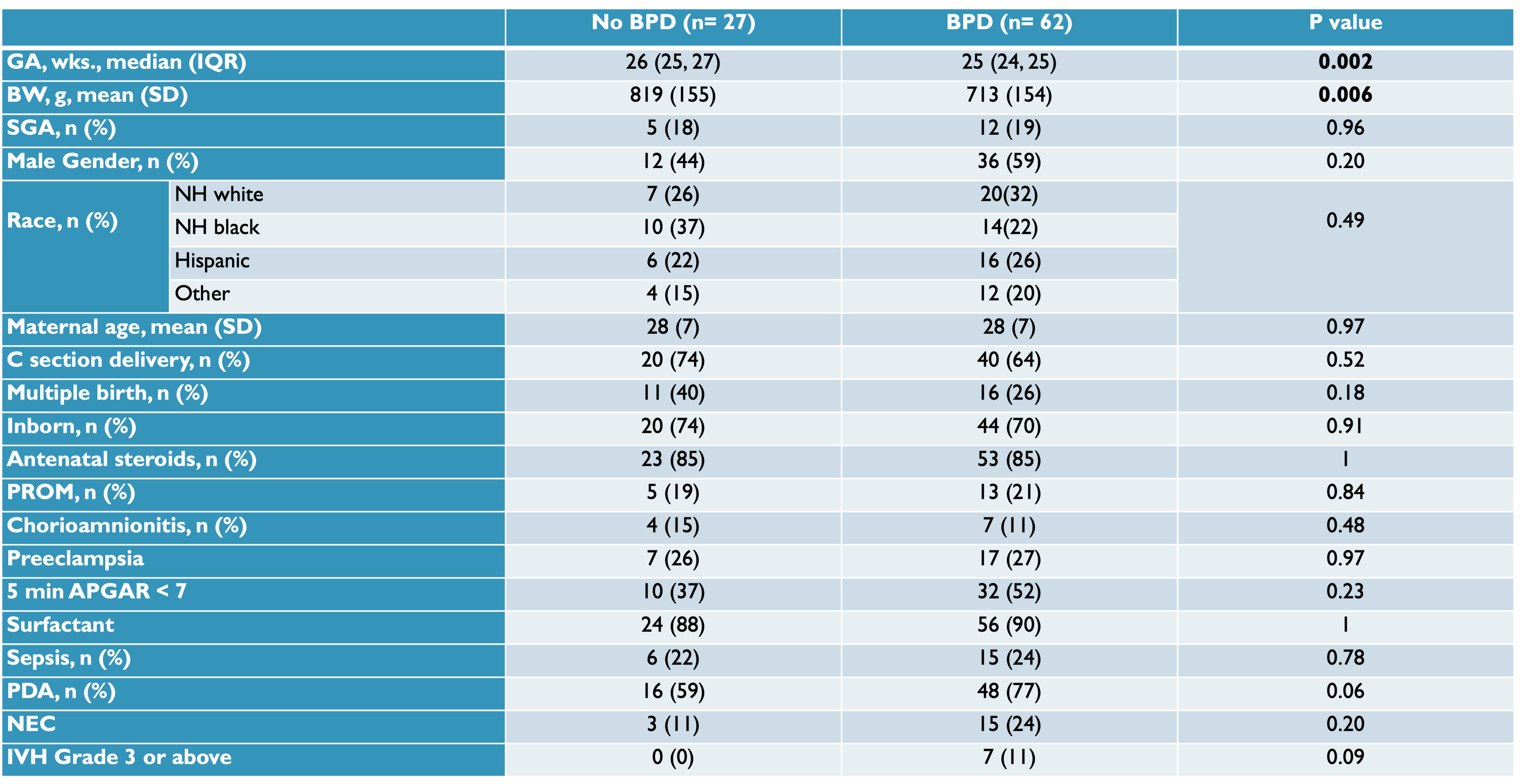
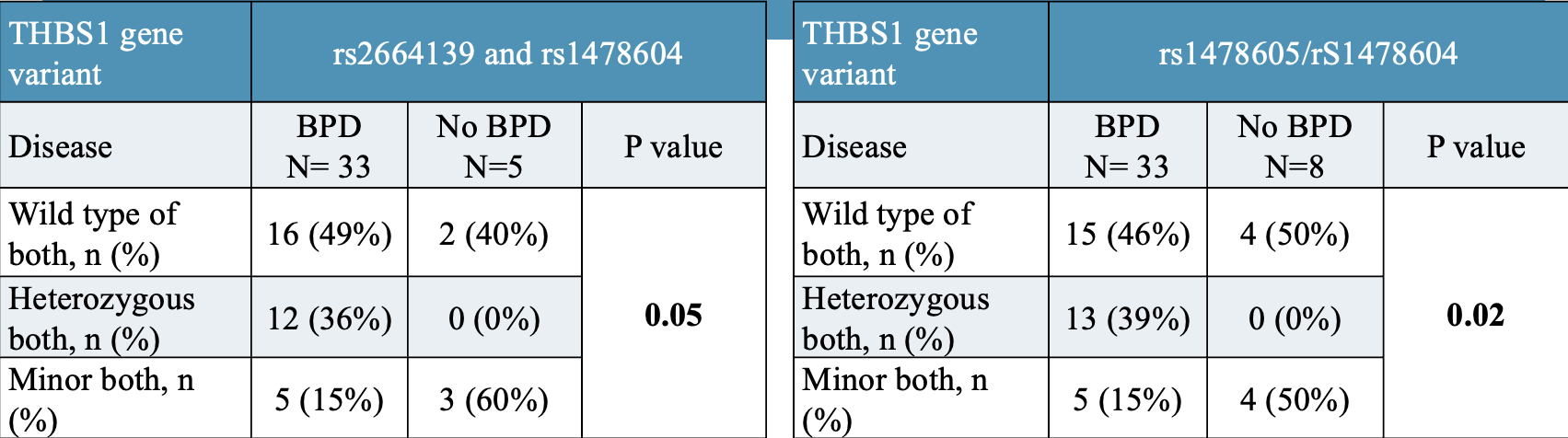
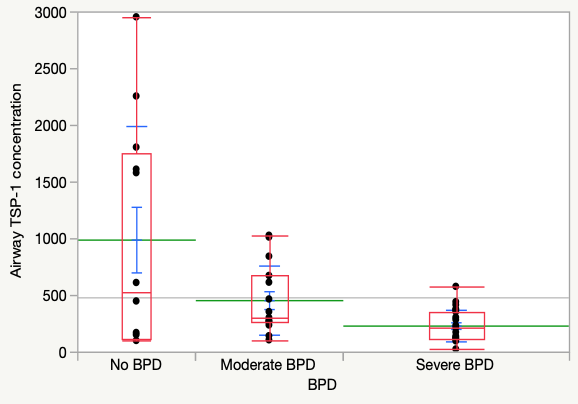
Results: Demographic characteristics as in Figure 1. ELBW infants with BPD had a significantly lower gestational age (25 vs 26 weeks, p= 0.002) and birth weight (713g vs 819g, p= 0.006). There was an increased incidence of BPD in the combination of the TT/TT genotype combination of THBS1 variants rs2664139/rs1478604 and the TT/GG genotype combination of THBS1 variants rs2664139/rs1478605. (Figure 2) The mean early airway protein level was 474 (+/- 583) ng/dl. Early airway TSP-1 protein levels were significantly different between the non-BPD(988 +/- 1002 ng/dl), moderate BPD (455 +/- 304 ng/dl), and severe BPD groups (230 +/- 139 ng/dl). TSP-1 protein concentration was significantly lower in infants with severe BPD. (Figure 3)
Conclusion(s): The combination of THBS1 variants was significantly associated with BPD. TSP-1 expression was significantly decreased in infants with severe BPD. These results may indicate a protective role of TSP-1 in BPD and have significant implications in personalized medicine.