Neonatology
Session: Neonatal Cardiology and Pulmonary Hypertension 1: PDA
83 - Periprocedural Clinical, Radiographic and Echocardiographic Characteristics of Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Occlusion of PDAs in the Neonatal Population
Sunday, May 5, 2024
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 83
Publication Number: 83.2068
Publication Number: 83.2068
- MW
Mollie Westrick, BA (she/her/hers)
Medical student
Emory University School of Medicine
Atlanta, Georgia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Premature patients have a high incidence of hemodynamically significant and persistently patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) that is associated with numerous comorbidities. Contemporary practice has shifted away from surgical closure and towards transcatheter device closure (TC). Despite the increasing frequency of PDA TC, few reports have characterized the hemodynamic, respiratory, and echocardiographic periprocedural characteristics in premature patients undergoing PDA TC.
Objective: We sought to describe the above-mentioned characteristics in a robust cohort of patients.
Design/Methods: This was a single center, retrospective study at a quaternary children’s hospital. Continuous variables were reported as medians with interquartile range (IQ). Frequencies and percentages were presented for categorical information.
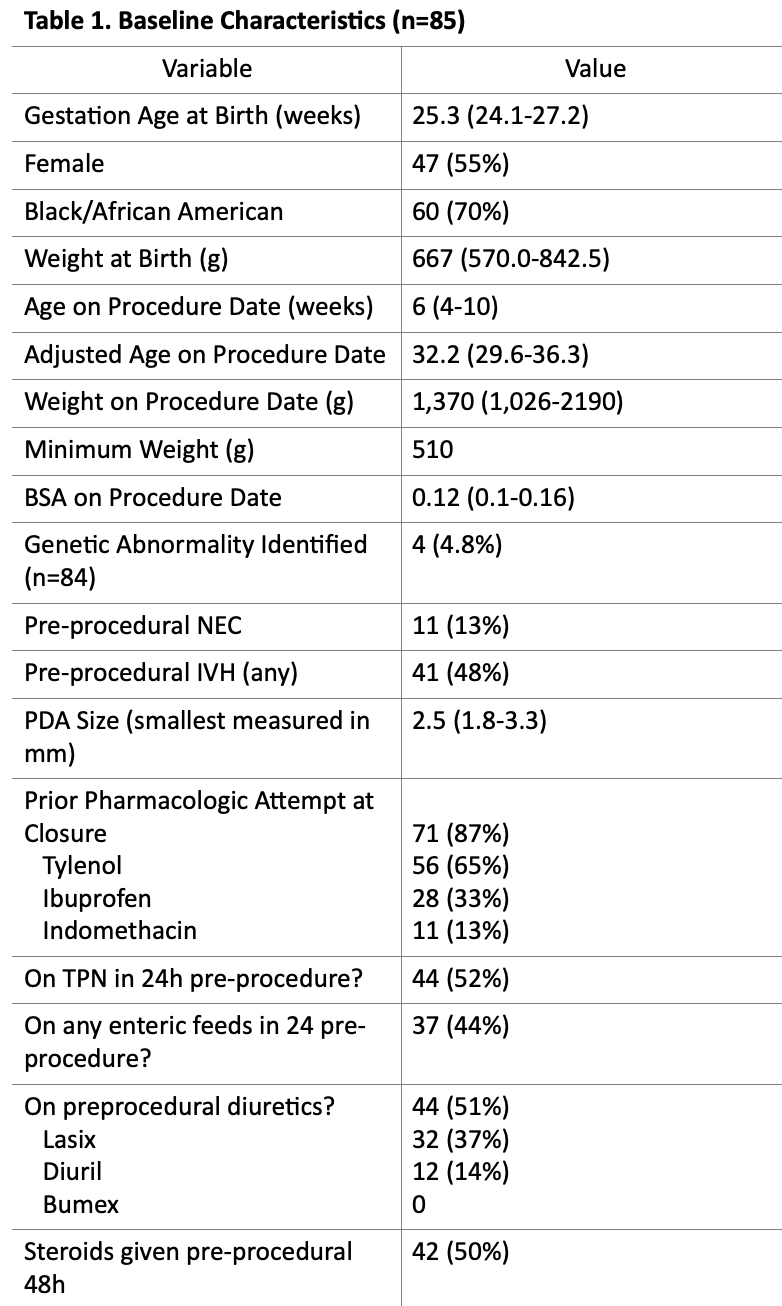
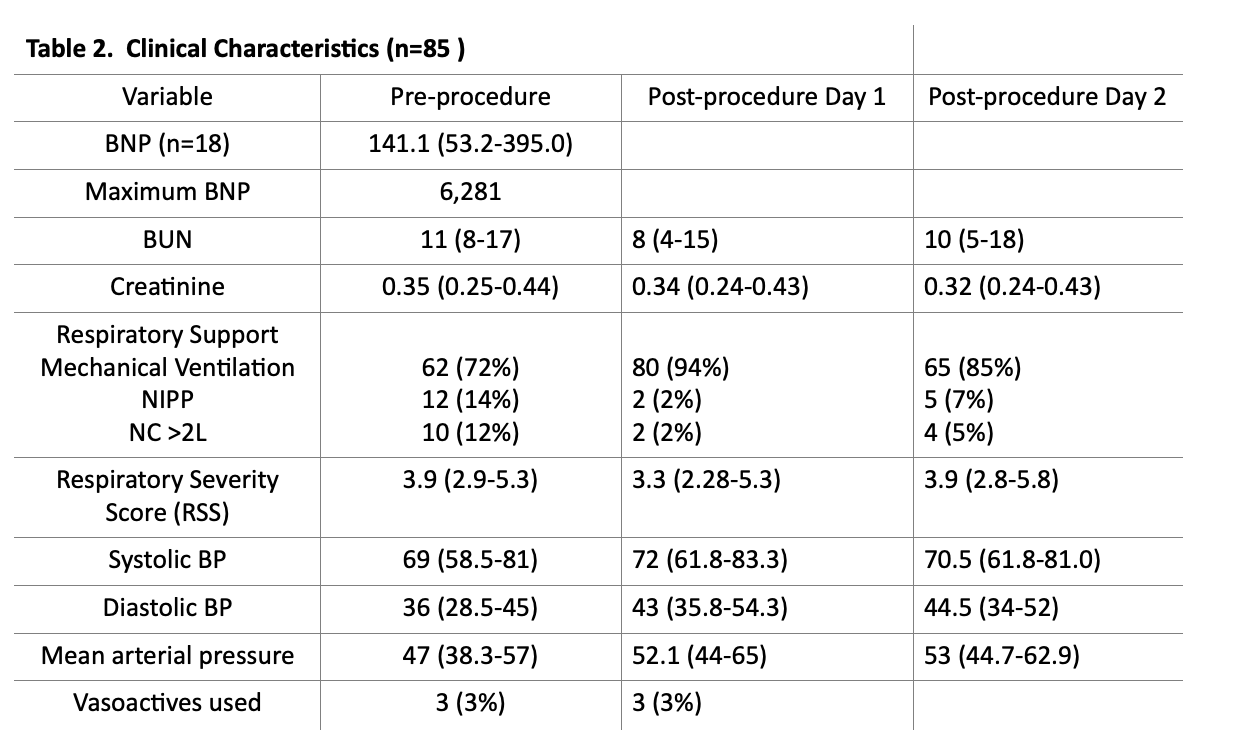
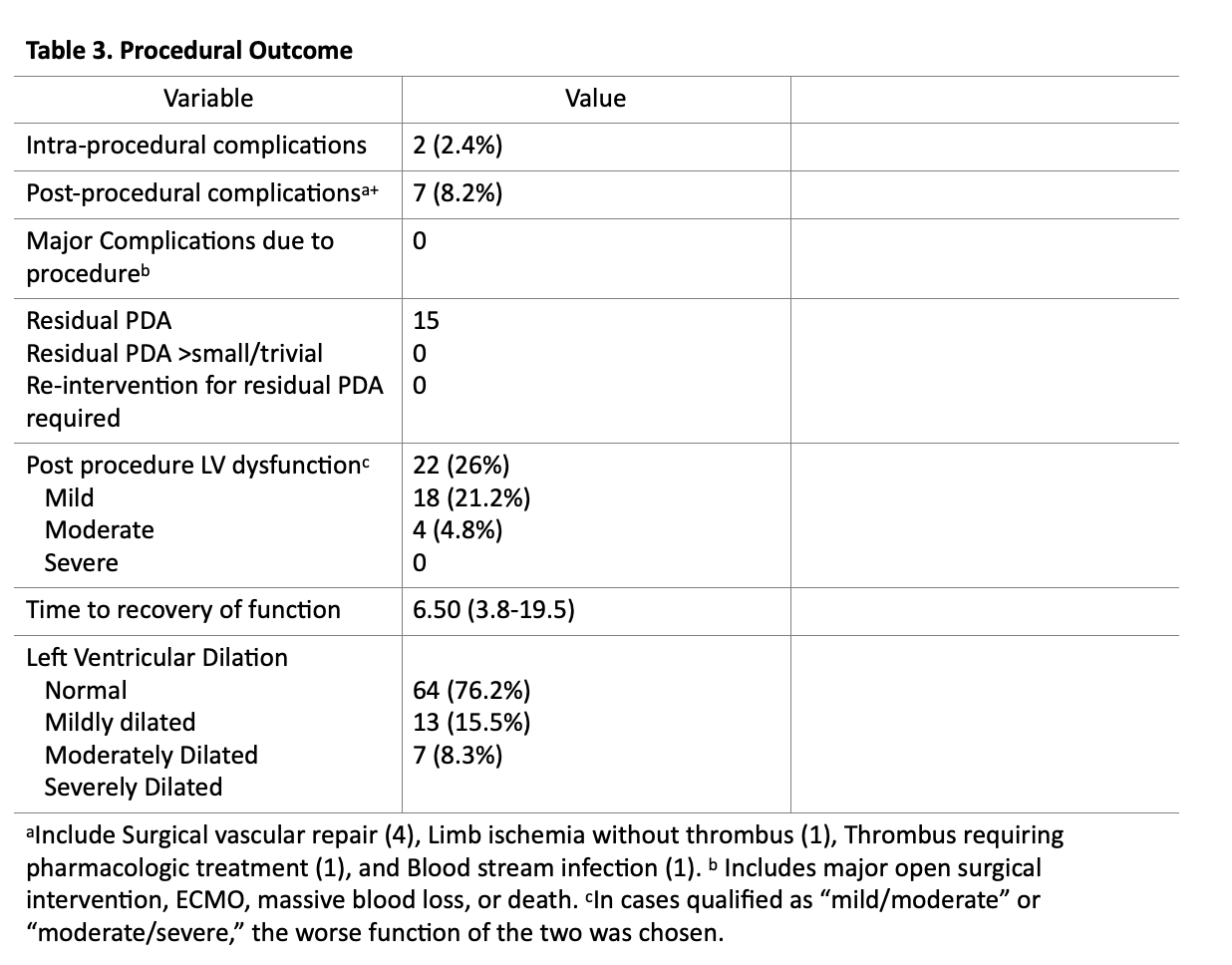
Results: A total of 85 patients underwent PDA TC between 9/1/2020 and 1/31/2023. The median weight and gestational age at birth was 667g (570,843) and 25.3 weeks (24.1,27.2), respectively. The median weight and adjusted age at the time of TC was 1.37 kg (1.03, 2.19) and 32.2 weeks (29.6-36.3),respectively. Pre-procedurally 62 (72%) of patients were mechanically ventilated with a respiratory severity score (RSS) of 3.9 (2.9-5.3). Post-procedurally 3 (3%) required vasoactive infusions and 22 (26%) developed ventricular dysfunction. 80 (94%) patients remained intubated by post procedure day 1, and 65 (85%) by day two. The vast majority (98%) underwent PDA TC without any intraprocedural complications or post procedural complications (92%). No patient required re-intervention for a residual PDA. Left ventricular dysfunction was noted in 22 (26%) of patients (18 mild, 2 mild/moderate, and 2 moderately depressed) with a median time to normalization of 6.5 (3.75-19.5) days.
Conclusion(s): In this cohort of small and premature patients, which is one of the largest reported thus far, PDA TC was safely performed in most patients with resolution of the PDA and a low complication rate. Further investigation is warranted to determine risk factors for significant complications and ideal timing of intervention.